vault backup: 2022-09-28 19:13:41
Affected files: .obsidian/workspace 03. Programming/COM/20210726 - COM Interface.md 03. Programming/DB/MySQL.md 03. Programming/DB/sqlite.md 03. Programming/Design Pattern.md 03. Programming/FFMPEG/00. Introduction.md 03. Programming/FFMPEG/01. Setup.md 03. Programming/FFMPEG/FFMpeg.md 03. Programming/Flask.md 03. Programming/Media Foundation/20210604 - Windows media foundation.md 03. Programming/OpenCV.md 03. Programming/OpenGL.md 03. Programming/Python/argparse.ArgumentParser.md 03. Programming/Python/decorator.md 03. Programming/Python/logging.md 03. Programming/Python/opencv.md 03. Programming/Python/subprocess.md 03. Programming/Python/threading.md 03. Programming/Python/tkinter.md 03. Programming/Python/檢測工具.md 03. Programming/QT/Dropdown button.md 03. Programming/QT/QVariant.md 03. Programming/QT/Qt.md 03. Programming/UML.md 03. Programming/演算法.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/blogHeader.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/date.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/front matter.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/note.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/table.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/thisWeek.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/日記.md 04. 資料收集/99. templates/讀書筆記.md 04. 資料收集/Linux/CLI/cut.md 04. 資料收集/Linux/CLI/scp.md 04. 資料收集/Linux/CLI/timedatectl.md 04. 資料收集/Linux/Programming.md 04. 資料收集/Linux/Ubuntu.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Hardware/RaspberryPi.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/Chrome.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/Obisidian.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/SublimeText.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/VirtualBox.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/Visual Studio Code.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/Windows Setup.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/Windows Terminal.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/freefilesync.md 04. 資料收集/Tool Setup/Software/vim.md 04. 資料收集/名言佳句.md 04. 資料收集/架站/Gitea.md 04. 資料收集/架站/HTTP Server/Apache.md 04. 資料收集/架站/HTTP Server/Nginx/Reverse Proxy(Layer4).md 04. 資料收集/架站/Pelican blog.md 04. 資料收集/架站/Proxmox VE.md 04. 資料收集/架站/SWAG Reverse proxy.md 04. 資料收集/架站/Storj.md 04. 資料收集/架站/Trojan.md 04. 資料收集/每週外食.md 04. 資料收集/科技/802.11.md 04. 資料收集/科技/HDR Sensor.md 04. 資料收集/科技/量子電腦.md 04. 資料收集/科技/鋰電池.md 04. 資料收集/興趣嗜好/RC/Traxxas Sledge.md 04. 資料收集/興趣嗜好/RC/好盈電變調整中立點.md 04. 資料收集/興趣嗜好/RC/差速器調教教學.md 04. 資料收集/興趣嗜好/模型/舊化作例.md 04. 資料收集/興趣嗜好/軍武/虎式.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20201201 - 學習如何學習.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20201218 - Kotlin權威2.0.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20201224 - 寫作是最好的自我投資.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20210119 - 中產悲歌.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20210220 - 最高學習法.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20210320 - 最高學以致用法.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20210406 - 精準購買.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20210723 - 高手學習.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20220526 - 深入淺出設計模式.md 04. 資料收集/讀書筆記/20220619 - 精確的力量.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/IPFS.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/MkDocs.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/Obsidian.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/docker.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/git/apply.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/git/submodule.md 04. 資料收集/軟體工具/youtube-dl.md 04. 資料收集/面試準備/技术面试最后反问面试官的话.md
This commit is contained in:
52
03. Programming/COM/20210726 - COM Interface.md
Normal file
52
03. Programming/COM/20210726 - COM Interface.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
## IID_PPV_ARGS Marco
|
||||
我们已经知道 CoCreateInstance 和 QueryInterface 函数的最后一个参数都是 void** 类型,这就会带来潜在的类型不匹配的安全问题,考虑下面的代码段:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// Wrong!
|
||||
|
||||
IFileOpenDialog *pFileOpen;
|
||||
|
||||
hr = CoCreateInstance(
|
||||
__uuidof(FileOpenDialog),
|
||||
NULL,
|
||||
CLSCTX_ALL,
|
||||
__uuidof(IFileDialogCustomize), // The IID does not match the pointer type!
|
||||
reinterpret_cast<void**>(&pFileOpen) // Coerce to void**.
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这段代码中,想要获取的接口类型是 IFileDialogCustomize,但是传入的却是一个 IFileOpenDialog 类型的指针变量。reinterpret_cast 表达式会绕过 C++ 类型系统的检测,所以编译器并不会主动抛出错误。
|
||||
|
||||
如果这段代码被运行,好的结果是函数返回失败,无法找到该接口;而坏的结果是,函数会返回成功,而你将获得一个类型结果不匹配的指针。换句话说,这个指针类型没有匹配到内存中真实的虚函数表,如果你所想不会有啥好事发生。
|
||||
|
||||
> 一个虚函数表(virtual method table)是一个函数指针表,它被用来实现 COM 组件运行期间的动态绑定。这种方式也是大多数 C++ 编译器用来实现动态绑定(多态)的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
IID_PPV_ARGS 宏是一个帮助你避免类型错误的方法,使用方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
__uuidof(IFileDialogCustomize), reinterpret_cast<void**>(&pFileOpen)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
替换为
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
IID_PPV_ARGS(&pFileOpen)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个宏会自动将 `__uuidof(IFileOpenDialog)` 参数插入。它可以保证你返回的接口指针类型的正确性。这是修改后的代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// Right.
|
||||
IFileOpenDialog *pFileOpen;
|
||||
hr = CoCreateInstance(__uuidof(FileOpenDialog), NULL, CLSCTX_ALL,
|
||||
IID_PPV_ARGS(&pFileOpen));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 QueryInterface 函数中使用一样的宏:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
IFileDialogCustomize *pCustom;
|
||||
hr = pFileOpen->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&pCustom));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 參考資料
|
||||
- [COM 编码实践 - 没事造轮子](https://wangzhechao.com/com-bian-ma-shi-jian/)
|
||||
134
03. Programming/DB/MySQL.md
Normal file
134
03. Programming/DB/MySQL.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
## Install MySQL
|
||||
- 下載MySQL: https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/installer/
|
||||
- 安裝
|
||||
- 安裝之後,執行MSQL Installer - Community
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210423152623.png]]
|
||||
- 選擇MySQL Server的Reconfigure
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210423152747.png]]
|
||||
- 依序設定port、帳號密碼。
|
||||
|
||||
## Install MariaDB
|
||||
1. `sudo apt install mariadb-server`
|
||||
2. Configuring MariaDB: `sudo mysql_secure_installation`
|
||||
這步驟會問幾個問題,大概是:
|
||||
1. 輸入目前root的密碼
|
||||
2. 是否要切換為unix_socket? -> No
|
||||
3. 要變更root的密碼嗎?-> No
|
||||
3. Testing MariaDB: `sudo systemctl status mariadb`
|
||||
4. Show version: `sudo mysqladmin version`
|
||||
|
||||
## Syntax
|
||||
### Basic
|
||||
login as root: `mysql -u root -p`
|
||||
|
||||
### User management
|
||||
#### Create user
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE USER 'testuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'test123test!';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remove user
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
DROP USER 'testuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Grant user's permission
|
||||
Below commands grant user's permission to *CREATE* and *DROP*.
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
GRANT CREATE ON *.* TO 'testuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
GRANT DROP ON tutorial_database.* TO 'testuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remove user's permission
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
REVOKE <permission> ON database.table FROM 'user'@'localhost';
|
||||
```
|
||||
上面命令中的`<permission>`必須替換成下面的其中一個:
|
||||
- ALL - Allow complete access to a specific database. If a database is not specified, then allow complete access to the entirety of MySQL.
|
||||
- CREATE - Allow a user to create databases and tables.
|
||||
- DELETE - Allow a user to delete rows from a table.
|
||||
- DROP - Allow a user to drop databases and tables.
|
||||
- EXECUTE - Allow a user to execute stored routines.
|
||||
- GRANT OPTION - Allow a user to grant or remove another user's privileges.
|
||||
- INSERT - Allow a user to insert rows from a table.
|
||||
- SELECT - Allow a user to select data from a database.
|
||||
- SHOW DATABASES- Allow a user to view a list of all databases.
|
||||
- UPDATE - Allow a user to update rows in a table.
|
||||
|
||||
例如:`REVOKE CREATE ON *.* FROM 'testuser'@'localhost';`
|
||||
最後,不要忘記`FLUSH PRIVILEGES;`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Show user's permission
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'testuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Change user's password
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
ALTER USER 'user-name'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NEW_USER_PASSWORD';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### View all users
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT User,Host FROM mysql.user;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Database
|
||||
#### Show all databases
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW DATABASES;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create table
|
||||
The rule:
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE tutorials_tbl(
|
||||
tutorial_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
|
||||
tutorial_title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
|
||||
tutorial_author VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
|
||||
submission_date DATE,
|
||||
PRIMARY KEY ( tutorial_id )
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
use autostation;
|
||||
CREATE TABLE station_state(
|
||||
id CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
ip CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
dhcp_ip CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
name CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
setupfilemd5 CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
setupfileversion CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
status CHAR(255) NOT NULL,
|
||||
update_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
|
||||
PRIMARY KEY ( id )
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Insert
|
||||
The rule:
|
||||
```
|
||||
INSERT INTO <table_name> ( field1, field2,...fieldN )
|
||||
VALUES
|
||||
( value1, value2,...valueN );
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
INSERT INTO client_state ( field1, field2,...fieldN )
|
||||
VALUES
|
||||
( value1, value2,...valueN );
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 參考
|
||||
- [Create a MySQL User on Linux via Command Line | Liquid Web](https://www.liquidweb.com/kb/create-a-mysql-user-on-linux-via-command-line/)
|
||||
- [Grant Permissions to a MySQL User on Linux via Command Line | Liquid Web](https://www.liquidweb.com/kb/grant-permissions-to-a-mysql-user-on-linux-via-command-line/)
|
||||
- [Remove Permissions for a MySQL User on Linux via Command Line - Liquid Web](https://www.liquidweb.com/kb/remove-permissions-for-a-mysql-user-on-linux-via-command-line/)
|
||||
- [Remove a MySQL User on Linux via Command Line - Liquid Web](https://www.liquidweb.com/kb/remove-a-mysql-user-on-linux-via-command-line/)
|
||||
13
03. Programming/DB/sqlite.md
Normal file
13
03. Programming/DB/sqlite.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## Build static library
|
||||
1. Navigate to [https://www.sqlite.org/download.html](https://www.sqlite.org/download.html) and download latest `amalgamation` source version of SQLite.
|
||||
2. Extract all the files into your project directory, or your include path, or separate path that you will add/added as include path in your project properties.
|
||||
3. Run `Developer Command Prompt for VS ****` which is usually available at `Start -> Programs -> Visual Studio **** -> Visual Studio Tools`.
|
||||
4. Navigate with command prompt to that directory where we extracted our SQLite.
|
||||
5. Run next command to compile: `cl /c /EHsc sqlite3.c`
|
||||
6. Run next command to create static library: `lib sqlite3.obj`
|
||||
7. Open properties of your project and add `sqlite3.lib` to `Linker -> Input -> Additional Dependencies`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you ready to include and use `sqlite3.h` in your project.
|
||||
|
||||
### 參考
|
||||
- [How to add SQLite into your VS project as Static Library](https://gist.github.com/payalord/c87cbd1d12ea7712449657d1c6583e12)
|
||||
240
03. Programming/Design Pattern.md
Normal file
240
03. Programming/Design Pattern.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
aliases:
|
||||
date: 2022-05-26
|
||||
time: 15:12:04
|
||||
description:
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 策略模式(Strategy)
|
||||
策略模式可以提供不一樣的演算法,但是又不用更改程式。
|
||||
以常見的鴨子為例,有一個基礎類別Duck,如何衍生出會飛得鴨子跟不會飛的鴨子?抑或是會叫的跟不會叫的?
|
||||
第一部是將會變動的部份分離出來,讓鴨子類別不需要去在乎飛跟叫的問題。
|
||||
再來是把飛跟叫的部份包裝成另一個class,並以之為基礎類別來實做出「實際的類別」。 ^e59e9f
|
||||
|
||||
以一般C++的override方法,會用的方式大致是這樣:
|
||||
|
||||
- !!!col
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 基礎類別
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duck {
|
||||
duck() {}
|
||||
void fly() {}
|
||||
void makeSound() {}
|
||||
void run() {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 衍生類別,遙控鴨子,會飛不會叫
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duckRC : public duck {
|
||||
duckRC() {}
|
||||
void fly() { printf("I can fly"); }
|
||||
void makeSound() { printf("I cannot make sound!"); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 衍生類別,木頭鴨子,不會飛不會叫
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duckWood : public duck {
|
||||
duckWood() {}
|
||||
void fly() { printf("I cannot fly"); }
|
||||
void makeSound() { printf("I cannot make sound!"); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但是這樣的話如果基礎類別會更改的話,那麼子類別也全部都會受影響,例如,現在希望所有的鴨子都要有一個「跑」的功能,所以我們就在基礎類別裡加一個`run()`:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duck {
|
||||
void fly() {}
|
||||
void makeSound() {}
|
||||
void run() { printf("I can run"); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
結果現在木頭鴨子也能跑了,這不符合我們的設計,所以我們必須回頭更改木頭鴨子的程式,改成
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duckWood : public duck {
|
||||
void fly() { printf("I cannot fly"); }
|
||||
void makeSound() { printf("I cannot make sound!"); }
|
||||
void run() { printf("I cannot run!"); } // <- 要改!
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果我們類別很多,那麼就很可能有沒改到的漏網之魚,bug就發生了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 封裝變動的部份
|
||||
比較好的方法一旦類別寫完之後,我們就不要動它了,日後新增的功能也不可以影響到他。我們把「會變動」的部份分離出來,變成各自的類別。
|
||||
為了簡化,我們討論「飛」這個功能就好,「飛」只分成「會飛」跟「不會飛」2種類別:
|
||||
|
||||
- !!!col
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 基礎類別,IFly
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class IFly {
|
||||
void doFly() = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 衍生類別,CanFly
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class CanFly {
|
||||
void doFly() { printf("I can fly"); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 衍生類別,CannotFly
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class CannotFly {
|
||||
void doFly() { printf("I cannot fly"); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
回到鴨子的基礎類別這邊,基礎類別`duck`本來是直接擁有`fly()`這個member function,現在我們把他改成他擁有的是`IFly`:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duck {
|
||||
duck() {}
|
||||
fly() { fly->doFly() };
|
||||
IFly* fly = nullptr;
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重寫遙控鴨子這個衍生類別:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duckRC : public duck {
|
||||
duckRC() {
|
||||
this->fly = new CanFly();
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重寫木頭鴨子,不會飛,所以:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class duckWood : public duck {
|
||||
duckWood() {
|
||||
this->fly = new CannotFly();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
現在,不管是遙控鴨子或是木頭鴨子,在被呼叫`fly()`的時候,都是根據它fly的「實際類別」來動作,遙控鴨子的`fly()`呼叫的是`CanFly`的`doFly()`,木頭鴨子的`fly()`呼叫的是`CannotFly`的`doFly()`,它們的動作完全取決於他們初始化的方式,而他們初始化的方式則取決於你的產品定義,要是今天你需要不同的飛行方式,增加新的fly類別即可,不會影響到舊有的。要是鴨子基礎類別增加了新的行為,如run,那麼就幫鴨子基礎類別的`run()`加個什麼都不做的預設動作就好,反正舊有的鴨子衍生類別本來就對這個新行為沒反應。要是`CanFly`的定義改變了,那麼你就是改變了使用`CanFly`的所有類別,這是你的定義明確的改變了,不是有程式被「額外」的改變了。
|
||||
|
||||
- !!!col
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### 原本直接繼承的方式
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220526182952.png]]
|
||||
- 2
|
||||
### 封裝變動的部份
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220526183019.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
這樣做的另一個好處是fly的初始化是動態的,只要再多一個`set()` function就可以動態的切換實作,也就是說你可以從設定檔來決定你的鴨子要長什麼樣子。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 觀察者模式(Observer Pattern )
|
||||
有一個會產生變動的主角(subject),與一堆需要觀察變動的觀察者(Observer)。觀察者向主角註冊,當主角發生變化的時候,發後通知給觀察者。
|
||||
![[20220614154819_Observer_Pattern.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
Subject方面,attach() 就是註冊觀察者,也可以叫做 register()、add() 之類。
|
||||
detach() 用來移除用戶,也可以叫做 unregister()、remove() 之類。
|
||||
notify()則是當發生變化時,用來通知所有觀察者的實作。
|
||||
|
||||
觀察者方面必須實作 update() 才能收到通知。
|
||||
|
||||
## 裝飾者模式(Decorator Pattern)
|
||||
「裝飾者」通常與「被裝飾者」有同樣的界面,「裝飾者」會取代「被裝飾者」的界面,進而改變「被裝飾者」的行為。
|
||||
裝飾者模式讓物件可以動態的改變行為,進為符合不同的需求。
|
||||
以書上的例子來說,我們多種飲料,每種飲料都可以加上不同的配料。例如,有奶茶、綠茶、紅茶3種飲料,另外有珍珠、紅豆、綠豆、仙草4種配料,我們要如何設計出適合的類別來讓每種飲料都可以隨寄的搭配配料呢?
|
||||
|
||||
假設這樣寫:
|
||||
- !!!col
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### Ingredient class
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class IngredientBubble { ... };
|
||||
class IngredientRedbean { ... };
|
||||
class IngredientGreenbean { ... };
|
||||
class IngredientFairyGrass { ... };
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
### Beverage class
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Beverage {
|
||||
int32_t cost() { return cost; }
|
||||
int32_t cost;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class BeverageMilkTea : public Beverage { ... };
|
||||
class BeverageGreenTea : public Beverage { ... };
|
||||
class BeverageBlackTea : public Beverage {
|
||||
IngredientBubble* bubble;
|
||||
IngredientRedbean* redbean;
|
||||
IngredientGreenbean* greenbean;
|
||||
IngredientFairyGrass* fairyGrass;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
每個飲料的class裡面都將每個配料定義為一個 member,如果客人有加配料的話,我們就將配料實例化,假設奶茶加了珍珠:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class BeverageBlackTea {
|
||||
void addBubble() {
|
||||
if (!bubble) bubble = new IngredientBubble();
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要算價格的時候:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class BeverageBlackTea {
|
||||
int32_t cost() {
|
||||
if (bubble) cost += 10; // 珍珠要加10元
|
||||
if (redbean) cost += 5; // 紅豆要加10元
|
||||
if (greenbean) cost += 7; // 綠豆要加10元
|
||||
if (fairyGrass) cost += 9; // 珍珠要加10元
|
||||
return cost;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int32_t cost = 30; // 奶茶本身10元
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
這樣的問題是,每當有一種新配料出現,我們就要在奶茶類別裡修改至少2個 function:`addXXX()` 與 `cost()`,目前我們有3種飲料,所以要修改6個 function,更何況,如果客人要加2份珍珠怎麼辦?這明顯不利程式的維護,必須有一種方法讓程式的修改最小,讓寫好的程式不用被修改才行。
|
||||
|
||||
讓裝飾者模式來改善這個問題。首先讓配料跟飲料有同樣的界面,但是修改一下配料的 constructor,當然也要實作 `cost()`,畢竟每個配料的價格不同:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class IngredientBubble : public Beverage {
|
||||
IngredientBubble(Beverage* beverage) {
|
||||
this->beverage = beverage;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t cost() {
|
||||
return 10 + this->beverage->cost(); // 珍珠要加10元,在加上原本飲料的價錢
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Beverage* beverage;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
珍珠這個 class 的 constructor 的參數是任何一個 Beverage,現在飲料被包在珍珠裡面,由珍珠來決定飲料最後的價格是多少。現在我們可以動態的決定飲料的組成,假設點一杯紅茶,加一些配料:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
// 為了讓程式看起來簡單,這裡就先不考慮memory leak的問題...>_<
|
||||
BeverageBlackTea* berverge = new BeverageBlackTea(); // 點一杯紅茶
|
||||
IngredientBubble* berverge = new IngredientBubble(berverge); // 加珍珠
|
||||
IngredientRedbean* berverge = new IngredientRedbean(berverge); // 加紅豆
|
||||
IngredientFairyGrass* berverge = new IngredientFairyGrass(berverge); // 加仙草
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
return berverge->cost(); // 算價錢
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到第一個變數是飲料,然後被包珍珠裡面,變成珍珠紅茶,再被包到紅豆裡面,變成紅豆珍珠紅茶,再被包到仙草裡面,變成仙草紅豆珍珠紅茶,到這樣的好處是:
|
||||
1. 有新的配料就寫新配料的 class
|
||||
2. 因為可以動態的組合,原本寫好的飲料 class 就不用在去動它了,愈少修改,愈少 bug
|
||||
3. 我們可以動態的組合配料,要加2份以上也沒有問題
|
||||
17
03. Programming/FFMPEG/00. Introduction.md
Normal file
17
03. Programming/FFMPEG/00. Introduction.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
- [FFmpeg](https://www.ffmpeg.org/)
|
||||
- Open source
|
||||
- For handling multimedia files and streams
|
||||
- GPL/LGPS license
|
||||
- Inspired by MPEG(Moving Picture Experts Group), FF means "Fast Foward"
|
||||
- Libraries
|
||||
- libavcodec: Contain all the encoders and decoders
|
||||
- libavformat: Muxers and demuxers
|
||||
- libavfilter: Filters that you can use on your video and audio according to your requirements
|
||||
- libavdevice: Input and output devices
|
||||
- libavutil
|
||||
- libswscale
|
||||
- libswresample
|
||||
- Tools
|
||||
- ffmpeg: Main transcoding engine
|
||||
- ffplay: Minimum tool to play a video or audio
|
||||
- ffprobe: For inspecting medias and extract valuable information
|
||||
30
03. Programming/FFMPEG/01. Setup.md
Normal file
30
03. Programming/FFMPEG/01. Setup.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
FFmpeg doesn't support any official builds for any operation systems. You can build the codes from source, or use the prebuilt packages.
|
||||
|
||||
## From source
|
||||
Get source code from [snapshot](https://ffmpeg.org/releases/ffmpeg-snapshot.tar.bz2) or git(`git clone https://git.ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg.git ffmpeg`).
|
||||
|
||||
## From prebuilt packages
|
||||
### MacOS
|
||||
Use homebrew to install FFMPEG package
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install ffmpeg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt update ;\
|
||||
sudo apt install ffmpeg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows
|
||||
Goto https://www.ffmpeg.org/download.html, and
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220607105807.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
And then browser jumps to https://www.gyan.dev/ffmpeg/builds/, click [release build](https://www.gyan.dev/ffmpeg/builds/#release-builds), download **release-full**.
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220607110211.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
Unzip the file, then put the folder to anywhere you like, e.g. `C:\libs`, so the full path of ffmpeg packages should looks like: `C:\libs\ffmpeg-5.0.1-full_build`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Add to system variable
|
||||
Add the path of bin of ffmpeg packages to `PATH` system variable.
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220607110949.png]]
|
||||
301
03. Programming/FFMPEG/FFMpeg.md
Normal file
301
03. Programming/FFMPEG/FFMpeg.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
|
||||
## Initialization
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
av_register_all();
|
||||
avformat_network_init();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Command line
|
||||
利用FFMpeg來轉檔
|
||||
```
|
||||
ffmpeg -i <SOURCE.mp4> -t 10 -s <W>x<H> -pix_fmt <OUTPUT_FORMAT> <OUTPUT_FILENAME>
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `-i`:來源檔名
|
||||
- `-t`:影片長度(秒)
|
||||
- `-s`:影片大小,長x寬
|
||||
- `-pix_fmt`:輸出的影像格式
|
||||
|
||||
example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
ffmpeg -i test.mp4 -t 10 -s 240x128 -pix_fmt yuv420p out240x128.yuv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Open file
|
||||
使用`avformat_open_input()`來打開檔案。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
AVFormatContext* pFormatContext = NULL;
|
||||
char* path = "E:\\download\\Incredible Patagonia_1920x1080.mp4";
|
||||
AVDictionary* pDict = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
int result = avformat_open_input(&pFormatContext, path, NULL, &pDict);
|
||||
```
|
||||
若是開啟失敗`result`會是一個非0的值。可以用`av_strerror()`來印出詳細的錯誤訊息。例:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
char errorMsg[1024] = { 0 };
|
||||
av_strerror(result, errorMsg, sizeof(errorMsg) - 1);
|
||||
printf("Open file %s error, code = %d, message = %s\n", path, result, errorMsg);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Get file information
|
||||
用`avformat_find_stream_info()`來把檔案的video/audio相關訊息放到`AVFormatContext`裡面。例:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
result = avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatContext, NULL);
|
||||
```
|
||||
也可以用
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
av_dump_format(pFormatContext, 0, path, 0);
|
||||
```
|
||||
來直接印出相關訊息,不過這方法是Ffmpeg內定的,如果要印出自己想要的內容,就必須將`AVFormatContext`裡面的`AVStream`一一撈出來:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < pFormatContext->nb_streams; i++) {
|
||||
AVStream* avStream = pFormatContext->streams[i];
|
||||
|
||||
if (avStream->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {
|
||||
printf("Stream[%d] is a audio stream.\n", i);
|
||||
printf(" Sample rate: %d\n", avStream->codecpar->sample_rate);
|
||||
printf(" Format : %d\n", avStream->codecpar->format);
|
||||
printf(" Channels : %d\n", avStream->codecpar->channels);
|
||||
printf(" FPS : %d/%d\n", avStream->avg_frame_rate.num, avStream->avg_frame_rate.den);
|
||||
printf(" Frame Size : %d\n", avStream->codecpar->frame_size);
|
||||
printf(" Codec ID : %d\n", avStream->codecpar->codec_id);
|
||||
} else if (avStream->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
|
||||
printf("Stream[%d] is a video stream.\n", i);
|
||||
printf(" Width : %d\n", avStream->codecpar->width);
|
||||
printf(" Height: %d\n", avStream->codecpar->height);
|
||||
printf(" FPS : %d/%d\n", avStream->avg_frame_rate.num, avStream->avg_frame_rate.den);
|
||||
printf(" Codec ID: %d\n", avStream->codecpar->codec_id);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
這個for-loop可以找出檔案裡面的video stream index與audio stream index。
|
||||
|
||||
另一個找出video stream index與audio stream index的方法:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
int videoStream = av_find_best_stream(pFormatContext, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1, NULL, 0);
|
||||
int audioStream = av_find_best_stream(pFormatContext, AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, -1, -1, NULL, 0);
|
||||
printf("Found best video stream index: %d\n", videoStream);
|
||||
printf("Found best audio stream index: %d\n", audioStream);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Demux
|
||||
### 重要結構
|
||||
#### AVPackt
|
||||
##### 重要的member:
|
||||
- `AVBufferRef *buf`:buffer的reference count,基本上不會用到。
|
||||
- `int64_t pts`:顯示順序
|
||||
- `int64_t dts`:decode順序
|
||||
- `uint8_t *data`:實際存data的buffer
|
||||
- `int size`:上面那個buffer的大小
|
||||
|
||||
##### 操作function
|
||||
- `AVPacket* av_packet_alloc()`:產生一個兂的AVPacket
|
||||
- `AVPacket* av_packet_clone(const AVPacket*)`:複製一個AVPacket
|
||||
- `int av_packet_ref(AVPacket*, const AVPacket*)`:增加reference count
|
||||
- `av_packet_unref(AVPacket*)`:減少reference count
|
||||
- `void av_packet_free(AVPacket**)`:釋放AVPacket
|
||||
- `void av_init_packet(AVPacket*)`:初始化AVPacket
|
||||
- `int av_packet_from_data(AVPacket*, uint8_t*, int size)`:從自己的data
|
||||
- `av_seek_frame`:
|
||||
- `AVFormatContext*`
|
||||
- `int stream_index`:要seek的stream
|
||||
- `int64_t timestamp`:timestamp
|
||||
- `int flag`:seek的方法
|
||||
- `#define AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD 1`:往後找
|
||||
- `#define AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE 2`:以byte為單位,跳到timestamp相對應的byte
|
||||
- `#define AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY 4`:跳到任意frame,不一定要key frame
|
||||
- `#define AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME 8`:依照frame number來找
|
||||
|
||||
## Decode
|
||||
### 重要結構
|
||||
#### AVCodecContext
|
||||
##### 重要的member
|
||||
- `int thread_count`:執行續的數量
|
||||
- `AVRational time_base`
|
||||
|
||||
##### 操作function
|
||||
- `avcodec_register_all()`:註冊所有的decoder。
|
||||
- `AVCodec* avcodec_find_decoder(enum AVCodecID)`:用codec ID來找到相對應的codec instance
|
||||
- `AVCodec* avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(const char* name)`:用codec的名子來找到相對應的codec instance
|
||||
- `AVCodecContext* avcodec_alloc_context3(const AVCodec*)`:用codec來建立`AVCodecContext`,codec只是用來解碼,解碼之後的相關資料要放在`AVCodecContext`裡面。
|
||||
- `void avcodec_free_context(AVCodecContext**)`:釋放`AVCodecContext`。
|
||||
- `int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext*, const AVCodec*, AVDictionary*)`
|
||||
- 開始解碼
|
||||
- `AVDictionary`的選項請看`libavcodec/options_table.h`
|
||||
|
||||
#### AVFrame
|
||||
##### 重要的member
|
||||
- `uint8_t* data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]`:存放這個frame的資料
|
||||
- `int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]`:存放指向各個plane的pointer
|
||||
- Plane mode
|
||||
- For video
|
||||
- 0:Y
|
||||
- 1:U
|
||||
- 2:V
|
||||
- 3:NULL
|
||||
- For audio
|
||||
- 0:Left channel
|
||||
- 1:Right channel
|
||||
- 2:NULL
|
||||
- Non plane mode
|
||||
- For video
|
||||
- 0:RGB RGB RGB
|
||||
- 1:NULL
|
||||
- `int width`:For video, frame width
|
||||
- `int height`:For video, frame height
|
||||
- `int nb_samples`:For audio
|
||||
- `int64_t pts`:這個frame的pts
|
||||
- `int64_t pkt_dts`:Packet的dts
|
||||
- `int sample_rate`:For audio,sampling rate
|
||||
- `uint64_t channel_layout`:For audio
|
||||
- `int channels`:For audio
|
||||
- `int format`:For video it's AVPixelFormat, for audio it's AVSampleFormat
|
||||
|
||||
##### 操作function
|
||||
- `AVFrame* av_frame_alloc()`:
|
||||
- `void av_frame_free(AVFrame*)`:
|
||||
- `AVFrame* av_frame_clone(const AVFrame*)`:
|
||||
- `int av_frame_ref(AVFrame* dst, const AVFrame* src)`:
|
||||
- `void av_frame_unref(AVFrame*)`:
|
||||
- `int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext*, const AVPacket*)`
|
||||
- `int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext*, AVFrame*)`
|
||||
|
||||
## Frame scaling
|
||||
##### 操作function
|
||||
- `sws_getContext`
|
||||
- `sws_getCachedContext`
|
||||
```
|
||||
SwsContext* sws_getCachedContext(
|
||||
SwsContext*,
|
||||
int srcW, int srcH, enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat,
|
||||
int dstW, int dstH, enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat,
|
||||
int flags,
|
||||
SwsFilter srcFilter,
|
||||
SwsFilter dstFilter,
|
||||
const double* param)
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `sws_scale`
|
||||
```
|
||||
int sws_scale(
|
||||
SwsContext*,
|
||||
const uint8_t* const srcSlice[], // 來源buffer的pointer, 如果是plane mode,要丟srcSlice[3]
|
||||
const int srcStride[], // linesize
|
||||
int srcSliceY,
|
||||
int srcSliceH, // image height
|
||||
uint8_t* const dst[], // 目標buffer的pointer, 如果是plane mode,要丟dst[3]
|
||||
const int dstStride[]) // linesize
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `void sws_freeContext(SwsContext*)`
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio resampling
|
||||
- `SwrContext* swr_alloc()`
|
||||
- `swr_alloc_set_opts`
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
SwrContext* swr_alloc_set_opts(
|
||||
SwrContext*,
|
||||
int64_t out_ch_layout, // Output
|
||||
AVSampleFormat outSampleFormat, // Output
|
||||
int outSampleRate, // Output
|
||||
int64_t in_ch_layout, // Input
|
||||
AVSampleFormat inSampleFormat, // Input
|
||||
int inSampleRate, // Input
|
||||
int log_offset, // 一般丟0
|
||||
void* log_ctx) // 一般丟0
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `int swr_init(SwrContext*)`
|
||||
- `void swr_free(SwrContext**)`
|
||||
- `swr_convert`
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
int swt_convert(
|
||||
SwrContext*,
|
||||
uint8_t** outData,
|
||||
int outCount, // Sample count for one channel
|
||||
uint8_t** inData,
|
||||
int inCount) // Sample count for one channel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio 播放
|
||||
### 會用到的class
|
||||
#### QAudioFormat
|
||||
- `setSampleRate`
|
||||
- `setSampleSize`
|
||||
- `setChannelCount`
|
||||
- `setCodec("audio/pcm")`
|
||||
- `setByteOrder(QAudioFormat::LittleEndian)`
|
||||
- `setSampleType(QAudioFormat::UnSignedInt)`
|
||||
|
||||
#### QAudioOutput
|
||||
- Constuctor參數就是一個`QAudioFormat`
|
||||
- `QIODevice* start()`
|
||||
- `suspend()`
|
||||
- `resume()`
|
||||
- `bufferSize()`
|
||||
- `byteFree()`
|
||||
- `periodSize()`
|
||||
|
||||
#### QIODevice
|
||||
- `qint64 write(const char* data, qint64 len)`
|
||||
|
||||
#### QBuffer
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QBuffer buffer;
|
||||
|
||||
if (buffer.open(QIODevice::ReadWrite)) {
|
||||
qInfo() << "Buffer Opened!";
|
||||
QByteArray data("Hello World");
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
|
||||
buffer.write(data);
|
||||
buffer.write("\r\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
//File and device access you may need to flush the data to the device
|
||||
//buffer.flush()
|
||||
|
||||
//Move to the first position
|
||||
buffer.seek(0);
|
||||
|
||||
qInfo() << buffer.readAll(); // retuen a QVariant
|
||||
qInfo() << "closing the buffer";
|
||||
|
||||
//ALWAYS close your device!
|
||||
buffer.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QAudioFormat audioFormat;
|
||||
audioFormat.setSampleRate(44100);
|
||||
audioFormat.setSampleSize(16);
|
||||
audioFormat.setChannelCount(2);
|
||||
audioFormat.setCodec("audio/pcm");
|
||||
audioFormat.setByteOrder(QAudioFormat::LittleEndian);
|
||||
audioFormat.setSampleType(QAudioFormat::UnSignedInt);
|
||||
|
||||
QAudioOutput* audioOutput = new QAudioOutput(audioFormat);
|
||||
QIODevice* ioDevice = audioOutput->start();
|
||||
|
||||
int size = audioOutput->periodSize();
|
||||
char* buffer = new char[size];
|
||||
FILE *pFile = fopen("E:\\download\\out.pcm", "rb");
|
||||
while (!feof(pFile)) {
|
||||
if (audioOutput->bytesFree() < size) {
|
||||
QThread::msleep(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
qint64 len = fread(buffer, 1, size, pFile);
|
||||
if (len <= 0) {
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ioDevice->write(buffer, len);
|
||||
}
|
||||
fclose(pFile);
|
||||
delete buffer;
|
||||
buffer = NULL;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用FFmpeg decode audio
|
||||
- [音视频开发之旅(60) -调试分析FFmpeg (解封装部分的)常用结构体](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/441055685)
|
||||
|
||||
## 參考資料
|
||||
- [mpv.io](https://mpv.io/)
|
||||
- [《FFmpeg基础知识》](https://opensourcelibs.com/lib/zhangfangtaozft-ffmpeg)
|
||||
- [ffmpeg - 专题 - 简书](https://www.jianshu.com/c/21a6fafc8ee3)
|
||||
206
03. Programming/Flask.md
Normal file
206
03. Programming/Flask.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
## 執行
|
||||
### Linux
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export FLASK_APP=RobotRunAutoServer.py
|
||||
export FLASK_DEBUG=1
|
||||
flask run --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows
|
||||
```
|
||||
set FLASK_APP=RobotRunAutoServer.py
|
||||
set FLASK_DEBUG=1
|
||||
flask run --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 路由
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@app.route('/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
return 'Index Page'
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/query/<SOMETHING>', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
|
||||
def query(SOMETHING):
|
||||
return 'Hello, {}!'.format(SOMETHING)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 靜態檔案
|
||||
```
|
||||
url_for('static', filename='style.css')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 模板
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from flask import render_template
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/hello/<name>')
|
||||
def hello(name=None):
|
||||
return render_template('hello.html', name=name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
依照 Flask 的慣例,它會在 templates 資料夾內去找模板檔,而 templates 資料夾的位置會根據這支 web app 是模組或是套件而有所不同。
|
||||
|
||||
如果是模組:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/application.py
|
||||
/templates
|
||||
/hello.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是套件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/application
|
||||
/__init__.py
|
||||
/templates
|
||||
/hello.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 存取 request 資料
|
||||
客戶端傳來的資料都放在 `request` 這個全域變數內,web app 利用 `request` 提供的資訊與客戶端互動。
|
||||
客戶端的 HTTP 方法存放在 `request` 的 `method` 屬性內,而 form 就存放在 `request` 的 `form` 屬性內。示例:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import request
|
||||
from flask import render_template
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
|
||||
def login():
|
||||
error = None
|
||||
if request.method == 'POST':
|
||||
if valid_login(request.form['username'], request.form['password']):
|
||||
return log_the_user_in(request.form['username'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
error = 'Invalid username / password'
|
||||
# the code below is executed if the request method was GET or the credentials were invalid
|
||||
return render_template('login.html', error=error)
|
||||
```
|
||||
如果 `form` 屬性不存在,伺服器端會引發 `KeyError` 錯誤,客戶端則會收到 HTTP 400 錯誤。
|
||||
|
||||
如果是要取用 `URL` 參數,則使用 `args` 屬性內的 `get()` 方法:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
searchword = request.args.get('key', '')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是要取用客戶端上傳的檔案,先確定在前端 HTML 表單的設定正確的屬性 `enctype="multipart/form-data"`,瀏覽器才會正確的把檔案上傳。調用 `request` 的 `files` 屬性就可以調用到檔案:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import request
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
|
||||
def upload_file():
|
||||
if request.method == 'POST':
|
||||
f = request.files['the_file']
|
||||
f.save('/var/www/uploads/uploaded_file.txt')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`files` 本身是個 dictionary,所以必須呼叫它裡面的 key 才會接到真正的檔案,這個 `file` 物件的行為就像標準的 Python `file` 物件,但它有個 `save()` 方法讓我們把檔案存到自己想要的路徑。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要沿用客戶端上傳的檔名,則調用 `filename` 屬性,但由於檔名的不可預知,可能會有安全風險,最好用 Werkzeug 的 `secure_filename()` 方法過濾掉:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import request
|
||||
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
|
||||
def upload_file():
|
||||
if request.method == 'POST':
|
||||
f = request.files['the_file']
|
||||
f.save('/var/www/uploads/' + secure_filename(f.filename))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果是要讀取 cookie 就調用 `request` 物件的 `cookies` 屬性,如果是要設置 cookie 就用 `response` 物件的 `set_cookie()` 方法。
|
||||
|
||||
`request` 的 `cookies` 也是一個 dictionary,裡面放了所有可以調用的 cookie。
|
||||
|
||||
但是如果想使用 session 的話,Flask 有提供更完善的 session 機制可以利用,不要手工用 cookie 來管理 session。
|
||||
|
||||
讀取 cookie 的範例:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import request
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
username = request.cookies.get('username')
|
||||
# use cookies.get(key) instead of cookies[key] to not get a KeyError if the cookie is missing.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
存入 cookie 的範例:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
@app.route('/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
resp = make_response(render_template(...))
|
||||
resp.set_cookie('username', 'the username')
|
||||
return resp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 重導頁面與錯誤頁面
|
||||
要重導使用 `redirect()` 方法,要中斷並報錯用 `abort()` 方法:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import abort, redirect, url_for
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
return redirect(url_for('login'))
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/login')
|
||||
def login():
|
||||
abort(401)
|
||||
this_is_never_executed()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果不想使用 Flask 預設的陽春錯誤頁,則利用 `errorhandler()` 修飾子來做客製:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import render_template
|
||||
|
||||
@app.errorhandler(404)
|
||||
def page_not_found(error):
|
||||
return render_template('page_not_found.html'), 404
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意到 `return` 那行最後面的 `404`,雖然上面的修飾子已經是 404,但 `return` 後面還是要加 `404` Flask 才認得這是 404 錯誤頁。
|
||||
|
||||
## Session
|
||||
Session 用來紀錄、辨識用戶的活動,實現方式是加密過的 cookie。
|
||||
|
||||
得先設置密鑰才能使用 session:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from flask import Flask, session, redirect, url_for, escape, request
|
||||
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
|
||||
|
||||
app = Flask(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the secret key to some random bytes. Keep this really secret!
|
||||
app.secret_key = b'_5#y2L"F4Q8z\n\xec]/'
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
if 'username' in session:
|
||||
return f"Logged in as {escape(session['username'])}"
|
||||
return 'You are not logged in'
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
|
||||
def login():
|
||||
if request.method == 'POST':
|
||||
session['username'] = request.form['username']
|
||||
return redirect(url_for('index'))
|
||||
return '''
|
||||
<form method="post">
|
||||
<p><input type=text name=username>
|
||||
<p><input type=submit value=Login>
|
||||
</form>
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
@app.route('/logout')
|
||||
def logout():
|
||||
# remove the username from the session if it's there
|
||||
session.pop('username', None)
|
||||
return redirect(url_for('index'))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
前面模板的章節有說過,模板引擎會幫我們把表單的 HTML 過濾掉,而在這裡沒有使用模板引擎,所以手動調用了 `escape()` 方法來濾掉 HTML 碼。
|
||||
|
||||
最後附註一點,瀏覽器可能會限制單一 cookie 容量,如果發現某個值應該要有卻調用不出來的話,想想看是不是超過 cookie 的容量上限了。
|
||||
|
||||
## Log 紀錄
|
||||
Flask app 物件有使用 Python 內建的 `logger` 模組,可以簡單調用:
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
app.logger.debug('A value for debugging')
|
||||
app.logger.warning('A warning occurred (%d apples)', 42)
|
||||
app.logger.error('An error occurred')
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
|
||||
- [媒體基礎程式設計指南 - Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs](https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-tw/windows/win32/medfound/media-foundation-programming-guide)
|
||||
|
||||
## 研究MFVideoEVRWebcam.cpp
|
||||
- IMFActivate: 代表實際的device,但是實際的device object是在`IMFActivate->ActivateObject()`才真的建立。
|
||||
- IID_PPV_ARGS:取得interface的IID value,並取得其pointer。詳細參考:[[20210726 - COM Interface#IID_PPV_ARGS Marco]]。
|
||||
-
|
||||
```
|
||||
CoInitializeEx
|
||||
MFStartup
|
||||
↳ ListVideoDevicesWithBriefFormat
|
||||
MFCreateAttributes(&pDeviceAttributes, 1)
|
||||
pDeviceAttributes->SetGUID()
|
||||
MFEnumDeviceSources(pDeviceAttributes, &ppDevices, &deviceCount)
|
||||
ppDevices[i]->GetAllocatedString
|
||||
ppDevices[i]->GetAllocatedString(MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_FRIENDLY_NAME, &friendlyName, &friendlyNameLength)
|
||||
ppDevices[i]->ActivateObject(IID_PPV_ARGS(&pMediaSource))
|
||||
MFCreateSourceReaderFromMediaSource(...)
|
||||
↳ ListModes
|
||||
pReader->GetNativeMediaType(0, dwMediaTypeIndex, &pType)
|
||||
↳ GetMediaTypeDescription
|
||||
pMediaType->GetMajorType(&MajorType)
|
||||
pMediaType->GetCount(&cAttrCount)
|
||||
MediaType->GetItemByIndex
|
||||
pMediaType->GetItemType
|
||||
↪ GetVideoTypeDescriptionBrief(...)
|
||||
pMediaType->GetGUID(MF_MT_SUBTYPE, &subType)
|
||||
MFGetAttributeSize(pMediaType, MF_MT_FRAME_SIZE, &width, &height)
|
||||
MFGetAttributeRatio(pMediaType, MF_MT_FRAME_RATE, &fpsNum, &fpsDen)
|
||||
↳ MFCreateVideoRendererActivate(_hwnd, &pActive)
|
||||
pActive->ActivateObject(IID_IMFMediaSink, (void**)&pVideoSink)
|
||||
pVideoSink->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IMFVideoRenderer), (void**)&pVideoRenderer)
|
||||
pVideoRenderer->InitializeRenderer(NULL, NULL)
|
||||
pVideoSink->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IMFGetService), (void**)&pService)
|
||||
pService->GetService(MR_VIDEO_RENDER_SERVICE, __uuidof(IMFVideoDisplayControl), (void**)&pVideoDisplayControl)
|
||||
pVideoDisplayControl->SetVideoWindow(_hwnd)
|
||||
pVideoDisplayControl->SetVideoPosition(NULL, &rc)
|
||||
pVideoSink->GetStreamSinkByIndex(0, &pStreamSink)
|
||||
pStreamSink->GetMediaTypeHandler(&pSinkMediaTypeHandler)
|
||||
pSinkMediaTypeHandler->GetMediaTypeCount(&sinkMediaTypeCount)
|
||||
GetVideoSourceFromDevice(WEBCAM_DEVICE_INDEX, &pVideoSource, &pVideoReader)
|
||||
↳
|
||||
pVideoReader->SetStreamSelection((DWORD)MF_SOURCE_READER_FIRST_VIDEO_STREAM, TRUE)
|
||||
pVideoSource->CreatePresentationDescriptor(&pSourcePresentationDescriptor)
|
||||
pSourcePresentationDescriptor->GetStreamDescriptorByIndex(0, &fSelected, &pSourceStreamDescriptor)
|
||||
pSourceStreamDescriptor->GetMediaTypeHandler(&pSourceMediaTypeHandler)
|
||||
pSourceMediaTypeHandler->GetMediaTypeCount(&srcMediaTypeCount)
|
||||
MFCreateMediaType(&pWebcamSourceType)
|
||||
FindMatchingVideoType(pSourceMediaTypeHandler, ...)
|
||||
↳
|
||||
pSourceMediaTypeHandler->IsMediaTypeSupported(pWebcamSourceType, &pWebCamMatchingType)
|
||||
pSourceMediaTypeHandler->SetCurrentMediaType(pWebCamMatchingType)
|
||||
pSourceMediaTypeHandler->SetCurrentMediaType(pWebcamSourceType)
|
||||
pSourceMediaTypeHandler->GetCurrentMediaType(&pVideoSourceOutputType)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 建立Video capture device
|
||||
### 1. 取得video capture的數量
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
IMFAttributes* pDeviceAttributes = NULL;
|
||||
IMFActivate** ppDevices = NULL;
|
||||
UINT32 deviceCount = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(MFCreateAttributes(&pDeviceAttributes, 1),
|
||||
"Error creating device attributes.");
|
||||
|
||||
// Request video capture devices.
|
||||
CHECK_HR(pDeviceAttributes->SetGUID(
|
||||
MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE,
|
||||
MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_VIDCAP_GUID),
|
||||
"Error initialising video configuration object.");
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(MFEnumDeviceSources(pDeviceAttributes, &ppDevices, &deviceCount),
|
||||
"Error enumerating devices.");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 用Symbolic來建立IMFActivate
|
||||
`MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_VIDCAP_SYMBOLIC_LINK`可以用來取得一個獨一無二的ID,相對的,也可以用來建立IMFActivate。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
IMFAttributes* pDeviceAttributes = NULL;
|
||||
IMFActivate* pDevice = NULL;
|
||||
UINT32 deviceCount = 0;
|
||||
bool result = false;
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(MFCreateAttributes(&pDeviceAttributes, 1),
|
||||
"Error creating device attributes.");
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(pDeviceAttributes->SetGUID(
|
||||
MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE,
|
||||
MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_VIDCAP_GUID),
|
||||
"Error initialising video configuration object.");
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(pDeviceAttributes->SetString(
|
||||
MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_VIDCAP_SYMBOLIC_LINK,
|
||||
deviceSymbolic.c_str()),
|
||||
"Error setting video capture symbolic link");
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_HR(MFCreateDeviceSourceActivate(pDeviceAttributes, &pDevice),
|
||||
"Error create activate device");
|
||||
```
|
||||
API:
|
||||
- [MFCreateDeviceSourceActivate function (mfidl.h)](https://docs.microsof.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/mfidl/nf-mfidl-mfcreatedevicesourceactivate)
|
||||
- [IMFAttributes::SetGUID (mfobjects.h)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/mfobjects/nf-mfobjects-imfattributes-setguid)
|
||||
- [IMFAttributes::SetString (mfobjects.h)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/mfobjects/nf-mfobjects-imfattributes-setstring)
|
||||
- [IMFAttributes::GetString (mfobjects.h)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/mfobjects/nf-mfobjects-imfattributes-getstring)
|
||||
|
||||
## 建立Audio capture device
|
||||
相對於video capture是用`MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_VIDCAP_SYMBOLIC_LINK`來建立IMFActivate,audio capture是用`MF_DEVSOURCE_ATTRIBUTE_SOURCE_TYPE_AUDCAP_ENDPOINT_ID`來建立獨一無二的ID
|
||||
|
||||
## IAMCameraControl interface
|
||||
使用`IAMCameraControl`來控制webcam的行為,例如曝光與[[20210604 - Windows media foundation#Pan Tilt Relative Control]]。
|
||||
|
||||
### Pan/Tilt Relative Control
|
||||
1. 需要先用`IMFMediaSource->QueryInterface()`取得`IID_IAMCameraControl`。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
hret = mfMediaSource->QueryInterface(
|
||||
IID_IAMCameraControl,
|
||||
(void**)&pCameraControl
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. 接下來就可以用`IAMCameraControl->GetRange()`、`Set()`、`Get()`來取得property,根據[CameraControlProperty](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/strmif/ne-strmif-cameracontrolproperty)可以看到可以用的property有:
|
||||
1. `CameraControl_Pan`
|
||||
2. `CameraControl_Tilt`
|
||||
3. `CameraControl_Roll`
|
||||
4. `CameraControl_Zoom`
|
||||
5. `CameraControl_Exposure`
|
||||
6. `CameraControl_Iris`
|
||||
7. `CameraControl_Focus`
|
||||
3. 但裡面並沒有關於PanRelative或是TiltRlative的控制,在google之後,在Stackoverflow上發現這篇:[Media Foundation Exposure in milliseconds](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63124813/media-foundation-exposure-in-milliseconds),裡面有人提到可以用ksmedia的property:`KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_EXTENDED_EXPOSUREMODE`(要使用這個property必須include `<ks.h>`與`<ksmedia.h>`),你會發現這個property定義在`<ksmedia.h>`裡面的`KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_EXTENDED_PROPERTY`這個enum裡面,然後順藤摸瓜的可以找到`KSPROPERTY_VIDCAP_CAMERACONTROL`這個enum,裡面就有定義`KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE`、`KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_TILT_RELATIVE`這些relative相關的東西了。
|
||||
4. 現在我們可以用`IAMCameraControl->GetRange()`來把`KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE`的值讀出來。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->GetRange(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
&min,
|
||||
&max,
|
||||
&steppingDelta,
|
||||
&default,
|
||||
&capsFlags
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
printf("min = %d\n", min); // get 1
|
||||
printf("max = %d\n", max); // get 1
|
||||
printf("steppingDelta = %d\n", steppingDelta); // get 1
|
||||
printf("default = %d\n", default); // get 1
|
||||
printf("capsFlags = %d\n", capsFlags); // get 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
但你會發現min、max的值都一樣。
|
||||
但是`IAMCameraControl->Set()`還是能用,用1跟-1來表示左轉與右轉。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->Set(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
-1, // or 1
|
||||
flag
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
5. `KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_TILT_RELATIVE`的控制方法跟Pan一樣,只是用1跟-1是表示上與下。
|
||||
6. Pan relative test code
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
HRESULT hret;
|
||||
IAMCameraControl* pCameraControl = NULL;
|
||||
|
||||
hret = mfMediaSource->QueryInterface(
|
||||
IID_IAMCameraControl,
|
||||
(void**)&pCameraControl
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
|
||||
long min;
|
||||
long max;
|
||||
long steppingDelta;
|
||||
long default;
|
||||
long capsFlags;
|
||||
long value;
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_EXTENDED_EXPOSUREMODE;
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->GetRange(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
&min,
|
||||
&max,
|
||||
&steppingDelta,
|
||||
&default,
|
||||
&capsFlags
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
printf("min = %d\n", min);
|
||||
printf("max = %d\n", max);
|
||||
printf("steppingDelta = %d\n", steppingDelta);
|
||||
printf("default = %d\n", default);
|
||||
printf("capsFlags = %d\n", capsFlags);
|
||||
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->Get(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
&value,
|
||||
&capsFlags
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("CameraControl_Pan hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
printf("value = %d\n", value);
|
||||
printf("capsFlags = 0x%08X\n", capsFlags);
|
||||
|
||||
long flag = CameraControl_Flags_Manual;
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->Set(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
-1,
|
||||
flag
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("pCameraControl->Set(KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE, -1) hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
Sleep(500);
|
||||
hret = pCameraControl->Set(
|
||||
KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE,
|
||||
1,
|
||||
flag
|
||||
);
|
||||
printf("pCameraControl->Set(KSPROPERTY_CAMERACONTROL_PAN_RELATIVE, 1) hret = 0x%08X\n", hret);
|
||||
Sleep(500);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## IAMVideoProcAmp interface
|
||||
使用`IAMVideoProcAmp`來控制webcam的影像相關部份。可以從[VideoProcAmpProperty enumeration](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/strmif/ne-strmif-videoprocampproperty)這個頁面看到詳細定義。節錄如下:
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Brightness`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Contrast`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Hue`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Saturation`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Sharpness`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Gamma`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_ColorEnable`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_WhiteBalance`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_BacklightCompensation`
|
||||
- `VideoProcAmp_Gain`
|
||||
389
03. Programming/OpenCV.md
Normal file
389
03. Programming/OpenCV.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,389 @@
|
||||
## Build code
|
||||
### 前置作業
|
||||
1. 要有NVIDIA GPU
|
||||
2. 安裝NVIDIA GPU driver
|
||||
3. 安裝[CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads)
|
||||
4. 安裝[cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-download)
|
||||
5. 安裝[CMake](https://cmake.org/download/)
|
||||
|
||||
### CMake && Visual Studio
|
||||
1. 下載OpenCV:[opencv](https://github.com/opencv/opencv)
|
||||
2. 解壓縮後放到`D:\temp\build_opencv\opencv-4.5.3\source`
|
||||
3. 建立`D:\temp\build_opencv\opencv-4.5.3\build`
|
||||
4. 下載OpenCV contrib:[opencv_contrib](https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib)
|
||||
5. 解壓縮後放到`D:\temp\build_opencv\opencv_contrib`
|
||||
6. 打開cmake-gui
|
||||
7. 如圖設定
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20210818115317.png]]
|
||||
8. 用`Add Entry`先加入以下define
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20210818115507.png]]
|
||||
如果是檔名,type就選FILEPATH,如果是目錄,type就選PATH
|
||||
- PYTHON3_EXECUTABLE=C:/python39/python.exe
|
||||
- PYTHON3_INCLUDE_DIR=C:/python39/include
|
||||
- PYTHON3_LIBRARY=C:/python39/libs/python39.lib
|
||||
- PYTHON3_NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS=C:/python39/Lib/site-packages/numpy/core/include
|
||||
- PYTHON3_PACKAGES_PATH=C:/python39/Lib/site-packages
|
||||
|
||||
如果要build win32 + Python 3.6.3 x86的話,改為以下設定:
|
||||
- PYTHON3_EXECUTABLE=C:/Python363/python.exe
|
||||
- PYTHON3_INCLUDE_DIR=C:/Python363/include
|
||||
- PYTHON3_LIBRARY=C:/Python363/libs/python36.lib
|
||||
- PYTHON3_NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS=C:/Python363/Lib/site-packages/numpy/core/include
|
||||
- PYTHON3_PACKAGES_PATH=C:/Python363/Lib/site-packages
|
||||
9. 按Configure,會跳出一個視窗,platform選x64
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20210818115809.png]]
|
||||
10. 這些要打勾
|
||||
- BUILD_opencv_world
|
||||
- BUILD_opencv_python3
|
||||
- OPENCV_DNN_CUDA
|
||||
- OPENCV_PYTHON3_VERSION
|
||||
- OPENCV_FORCE_PYTHON_LIBS
|
||||
- OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE
|
||||
- ENABLE_FAST_MATH
|
||||
- WITH_CUDA
|
||||
- WITH_OPENMP
|
||||
- OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv_contrib/modules
|
||||
11. 再按一次Configure,必須沒有錯誤的跑完,像是
|
||||
```
|
||||
General configuration for OpenCV 4.5.3 =====================================
|
||||
Version control: unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Extra modules:
|
||||
Location (extra): D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv_contrib/modules
|
||||
Version control (extra): 4.5.3-6-g907efb96
|
||||
|
||||
Platform:
|
||||
Timestamp: 2021-08-18T03:40:06Z
|
||||
Host: Windows 10.0.19043 AMD64
|
||||
CMake: 3.21.1
|
||||
CMake generator: Visual Studio 16 2019
|
||||
CMake build tool: C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Visual Studio/2019/Professional/MSBuild/Current/Bin/MSBuild.exe
|
||||
MSVC: 1929
|
||||
Configuration: Debug Release
|
||||
|
||||
CPU/HW features:
|
||||
Baseline: SSE SSE2 SSE3
|
||||
requested: SSE3
|
||||
Dispatched code generation: SSE4_1 SSE4_2 FP16 AVX AVX2 AVX512_SKX
|
||||
requested: SSE4_1 SSE4_2 AVX FP16 AVX2 AVX512_SKX
|
||||
SSE4_1 (17 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1
|
||||
SSE4_2 (2 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1 POPCNT SSE4_2
|
||||
FP16 (1 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1 POPCNT SSE4_2 FP16 AVX
|
||||
AVX (5 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1 POPCNT SSE4_2 AVX
|
||||
AVX2 (31 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1 POPCNT SSE4_2 FP16 FMA3 AVX AVX2
|
||||
AVX512_SKX (7 files): + SSSE3 SSE4_1 POPCNT SSE4_2 FP16 FMA3 AVX AVX2 AVX_512F AVX512_COMMON AVX512_SKX
|
||||
|
||||
C/C++:
|
||||
Built as dynamic libs?: YES
|
||||
C++ standard: 11
|
||||
C++ Compiler: C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Visual Studio/2019/Professional/VC/Tools/MSVC/14.29.30037/bin/Hostx64/x64/cl.exe (ver 19.29.30040.0)
|
||||
C++ flags (Release): /DWIN32 /D_WINDOWS /W4 /GR /D _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE /D _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_DEPRECATE /D _SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS /Gy /bigobj /Oi /fp:fast /EHa /wd4127 /wd4251 /wd4324 /wd4275 /wd4512 /wd4589 /MP /MD /O2 /Ob2 /DNDEBUG
|
||||
C++ flags (Debug): /DWIN32 /D_WINDOWS /W4 /GR /D _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE /D _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_DEPRECATE /D _SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS /Gy /bigobj /Oi /fp:fast /EHa /wd4127 /wd4251 /wd4324 /wd4275 /wd4512 /wd4589 /MP /MDd /Zi /Ob0 /Od /RTC1
|
||||
C Compiler: C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Visual Studio/2019/Professional/VC/Tools/MSVC/14.29.30037/bin/Hostx64/x64/cl.exe
|
||||
C flags (Release): /DWIN32 /D_WINDOWS /W3 /D _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE /D _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_DEPRECATE /D _SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS /Gy /bigobj /Oi /fp:fast /MP /MD /O2 /Ob2 /DNDEBUG
|
||||
C flags (Debug): /DWIN32 /D_WINDOWS /W3 /D _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE /D _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_DEPRECATE /D _SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS /Gy /bigobj /Oi /fp:fast /MP /MDd /Zi /Ob0 /Od /RTC1
|
||||
Linker flags (Release): /machine:x64 /INCREMENTAL:NO
|
||||
Linker flags (Debug): /machine:x64 /debug /INCREMENTAL
|
||||
ccache: NO
|
||||
Precompiled headers: NO
|
||||
Extra dependencies: cudart_static.lib nppc.lib nppial.lib nppicc.lib nppidei.lib nppif.lib nppig.lib nppim.lib nppist.lib nppisu.lib nppitc.lib npps.lib cublas.lib cudnn.lib cufft.lib -LIBPATH:C:/Program Files/NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit/CUDA/v11.4/lib/x64
|
||||
3rdparty dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
OpenCV modules:
|
||||
To be built: aruco barcode bgsegm bioinspired calib3d ccalib core cudaarithm cudabgsegm cudacodec cudafeatures2d cudafilters cudaimgproc cudalegacy cudaobjdetect cudaoptflow cudastereo cudawarping cudev datasets dnn dnn_objdetect dnn_superres dpm face features2d flann fuzzy gapi hfs highgui img_hash imgcodecs imgproc intensity_transform line_descriptor mcc ml objdetect optflow phase_unwrapping photo plot python3 quality rapid reg rgbd saliency shape stereo stitching structured_light superres surface_matching text tracking ts video videoio videostab wechat_qrcode world xfeatures2d ximgproc xobjdetect xphoto
|
||||
Disabled: -
|
||||
Disabled by dependency: -
|
||||
Unavailable: alphamat cvv freetype hdf java julia matlab ovis python2 python2 sfm viz
|
||||
Applications: tests perf_tests apps
|
||||
Documentation: NO
|
||||
Non-free algorithms: NO
|
||||
|
||||
Windows RT support: NO
|
||||
|
||||
GUI:
|
||||
Win32 UI: YES
|
||||
VTK support: NO
|
||||
|
||||
Media I/O:
|
||||
ZLib: build (ver 1.2.11)
|
||||
JPEG: build-libjpeg-turbo (ver 2.1.0-62)
|
||||
WEBP: build (ver encoder: 0x020f)
|
||||
PNG: build (ver 1.6.37)
|
||||
TIFF: build (ver 42 - 4.2.0)
|
||||
JPEG 2000: build (ver 2.4.0)
|
||||
OpenEXR: build (ver 2.3.0)
|
||||
HDR: YES
|
||||
SUNRASTER: YES
|
||||
PXM: YES
|
||||
PFM: YES
|
||||
|
||||
Video I/O:
|
||||
DC1394: NO
|
||||
FFMPEG: YES (prebuilt binaries)
|
||||
avcodec: YES (58.134.100)
|
||||
avformat: YES (58.76.100)
|
||||
avutil: YES (56.70.100)
|
||||
swscale: YES (5.9.100)
|
||||
avresample: YES (4.0.0)
|
||||
GStreamer: NO
|
||||
DirectShow: YES
|
||||
Media Foundation: YES
|
||||
DXVA: YES
|
||||
|
||||
Parallel framework: Concurrency
|
||||
|
||||
Trace: YES (with Intel ITT)
|
||||
|
||||
Other third-party libraries:
|
||||
Intel IPP: 2020.0.0 Gold [2020.0.0]
|
||||
at: D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv-4.5.3/build/3rdparty/ippicv/ippicv_win/icv
|
||||
Intel IPP IW: sources (2020.0.0)
|
||||
at: D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv-4.5.3/build/3rdparty/ippicv/ippicv_win/iw
|
||||
Lapack: NO
|
||||
Eigen: NO
|
||||
Custom HAL: NO
|
||||
Protobuf: build (3.5.1)
|
||||
|
||||
NVIDIA CUDA: YES (ver 11.4, CUFFT CUBLAS)
|
||||
NVIDIA GPU arch: 35 37 50 52 60 61 70 75 80 86
|
||||
NVIDIA PTX archs:
|
||||
|
||||
cuDNN: YES (ver 8.2.2)
|
||||
|
||||
OpenCL: YES (NVD3D11)
|
||||
Include path: D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv-4.5.3/source/3rdparty/include/opencl/1.2
|
||||
Link libraries: Dynamic load
|
||||
|
||||
Python 3:
|
||||
Interpreter: C:/python39/python.exe (ver 3.9.6)
|
||||
Libraries: C:/python39/libs/python39.lib (ver 3.9.6)
|
||||
numpy: C:/python39/Lib/site-packages/numpy/core/include (ver 1.19.5)
|
||||
install path: C:/python39/Lib/site-packages/cv2/python-3.9
|
||||
|
||||
Python (for build): C:/python39/python.exe
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
ant: NO
|
||||
JNI: NO
|
||||
Java wrappers: NO
|
||||
Java tests: NO
|
||||
|
||||
Install to: D:/temp/build_opencv/opencv-4.5.3/build/install
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring done
|
||||
```
|
||||
12. 按下Generate按鈕就會生sln檔案。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### CMake by command
|
||||
用command line的話就可以將多個平台一次編起來,不用一直改GUI。
|
||||
寫了一個`build.bat`可以編譯不同版本與平台:
|
||||
```bat
|
||||
rem build.bat
|
||||
echo on
|
||||
rem build.bat
|
||||
rem win32 ARCH=%1, win32/x64
|
||||
rem 15 VS_CODE=%2, 15/16
|
||||
rem 2017 VS_VERSION=%3, 2017/2019
|
||||
rem DEBUG BUILD_TYPE=%4, DEBUG/RELEASE
|
||||
rem "C:/Python363/python.exe" PYTHON3_EXE=%5
|
||||
rem "C:/Python363/include" PYTHON3_INCLUDE=%6
|
||||
rem "C:/Python363/libs/python36.lib" PYTHON3_LIB=%7
|
||||
rem "C:/Python363/Lib/site-packages/numpy/core/include" PYTHON3_NP_INCLUDE=%8
|
||||
rem "C:/Python363/Lib/site-packages" PYTHON3_PACKAGES=%9
|
||||
rem 3.6.3 PY_VERSION=%10
|
||||
rem 1 CLEAN_BUILD=%11, 1: Delete build folder, 0: Do nothing
|
||||
|
||||
set DO_CONFIG=1
|
||||
set DO_BUILD=1
|
||||
set ARCH=%1
|
||||
set VS_CODE=%2
|
||||
set VS_VERSION=%3
|
||||
set BUILD_TYPE=%4
|
||||
set PYTHON3_EXE=%5
|
||||
set PYTHON3_INCLUDE=%6
|
||||
set PYTHON3_LIB=%7
|
||||
set PYTHON3_NP_INCLUDE=%8
|
||||
set PYTHON3_PACKAGES=%9
|
||||
set GENERATOR="Visual Studio %VS_CODE% %VS_VERSION%"
|
||||
shift
|
||||
set PY_VERSION=%9
|
||||
set CV_VERSION=4.5.3
|
||||
set CV_SOURCE="opencv-%CV_VERSION%\source"
|
||||
set CV_BUILD=build\vs%VS_VERSION%.%ARCH%.%BUILD_TYPE%
|
||||
set CV_EXTRA_MODULES="opencv_contrib\modules"
|
||||
shift
|
||||
set CLEAN_BUILD=%9
|
||||
|
||||
if %CLEAN_BUILD% == 1 (
|
||||
rmdir /s /q %CV_BUILD%
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if %DO_CONFIG% == 1 (
|
||||
mkdir %CV_BUILD%
|
||||
|
||||
"C:\Program Files\CMake\bin\cmake.exe" ^
|
||||
-B%CV_BUILD% ^
|
||||
-H%CV_SOURCE% ^
|
||||
-G%GENERATOR% ^
|
||||
-A%ARCH% ^
|
||||
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=%BUILD_TYPE% ^
|
||||
-DOPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=%CV_EXTRA_MODULES% ^
|
||||
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%CV_BUILD% ^
|
||||
-DINSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=OFF ^
|
||||
-DINSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=OFF ^
|
||||
-DBUILD_opencv_python3=ON ^
|
||||
-DPYTHON3_EXECUTABLE=%PYTHON3_EXE% ^
|
||||
-DPYTHON3_INCLUDE_DIR=%PYTHON3_INCLUDE% ^
|
||||
-DPYTHON3_LIBRARY=%PYTHON3_LIB% ^
|
||||
-DPYTHON3_NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS=%PYTHON3_NP_INCLUDE% ^
|
||||
-DPYTHON3_PACKAGES_PATH=%PYTHON3_PACKAGES% ^
|
||||
-DOPENCV_PYTHON3_VERSION=%PY_VERSION% ^
|
||||
-DOPENCV_FORCE_PYTHON_LIBS=ON ^
|
||||
-DBUILD_opencv_world=ON ^
|
||||
-DOPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON ^
|
||||
-DENABLE_FAST_MATH=ON ^
|
||||
-DWITH_OPENMP=ON ^
|
||||
-DWITH_OPENGL=ON
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if %DO_BUILD% == 1 (
|
||||
"C:\Program Files\CMake\bin\cmake.exe" --build %CV_BUILD% --target INSTALL --config %BUILD_TYPE%
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
這樣以後就可以用參數的方法來設定,譬如要使用vs2019來編譯x64 release的話,就可以這樣下:
|
||||
```bat
|
||||
rem build_vs2019.x64.RELEASE.bat
|
||||
echo off
|
||||
rem ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
rem
|
||||
rem x64, RELEASE, 2019, CLEAN
|
||||
rem
|
||||
set ARCH=x64
|
||||
set VS_CODE=16
|
||||
set VS_VERSION=2019
|
||||
set BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE
|
||||
set PYTHON3_EXE="C:/Python39/python.exe"
|
||||
set PYTHON3_INCLUDE="C:/Python39/include"
|
||||
set PYTHON3_LIB="C:/Python39/libs/python39.lib"
|
||||
set PYTHON3_NP_INCLUDE="C:/Python39/Lib/site-packages/numpy/core/include"
|
||||
set PYTHON3_PACKAGES="C:/Python39/Lib/site-packages"
|
||||
set PY_VERSION=3.9
|
||||
set CLEAN_BUILD=1
|
||||
echo "============================================================"
|
||||
echo "Build %ARCH%.%VS_VERSION%(%VS_CODE%).%BUILD_TYPE%, Python=%PY_VERSION%, CLEAN_BUILD=%CLEAN_BUILD%"
|
||||
echo ""
|
||||
call build.bat ^
|
||||
%ARCH% %VS_CODE% %VS_VERSION% %BUILD_TYPE% %PYTHON3_EXE% ^
|
||||
%PYTHON3_INCLUDE% %PYTHON3_LIB% %PYTHON3_NP_INCLUDE% %PYTHON3_PACKAGES% ^
|
||||
%PY_VERSION% %CLEAN_BUILD%
|
||||
rem ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 參考
|
||||
- [Build OpenCV GPU Version On Windows 10](https://medium.com/chung-yi/build-opencv-gpu-version-on-windows-10-c37a33437525)
|
||||
- [Cannot install openCV 3.1.0 with python3. CMAKE not including or linking python correctly](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42638342/cannot-install-opencv-3-1-0-with-python3-cmake-not-including-or-linking-python)
|
||||
- [在Windows上编译带CUDA(GPU)的OpenCV](https://shaogui.life/2021/03/08/%E5%9C%A8Windows%E4%B8%8A%E7%BC%96%E8%AF%91%E5%B8%A6CUDA(GPU)%E7%9A%84opencv/)
|
||||
- [How to use OpenCV DNN Module with Nvidia GPU on Windows](https://learnopencv.com/how-to-use-opencv-dnn-module-with-nvidia-gpu-on-windows/)
|
||||
- [Accelerate OpenCV 4.5.0 on Windows – build with CUDA and python bindings - James Bowley](https://jamesbowley.co.uk/accelerate-opencv-4-5-0-on-windows-build-with-cuda-and-python-bindings/#python_bindings)
|
||||
|
||||
## 影像處理
|
||||
- sift
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def adjust_gamma(image, gamma=1.0):
|
||||
invGamma = 1.0 / gamma
|
||||
table = np.array([((i / 255.0) ** invGamma) * 255
|
||||
for i in np.arange(0, 256)]).astype("uint8")
|
||||
|
||||
return cv2.LUT(image, table)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sift_compare(path_a, path_b):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Use SIFT features to measure image similarity
|
||||
@args:
|
||||
{str} path_a: the path to an image file
|
||||
{str} path_b: the path to an image file
|
||||
@returns:
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
'''
|
||||
# initialize the sift feature detector
|
||||
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
|
||||
|
||||
# get the images
|
||||
img_a = cv2.imread(path_a)
|
||||
img_b = cv2.imread(path_b)
|
||||
img_a = adjust_gamma(img_a, 0.1)
|
||||
img_b = adjust_gamma(img_b, 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
# find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT
|
||||
kp_a, desc_a = orb.detectAndCompute(img_a, None)
|
||||
kp_b, desc_b = orb.detectAndCompute(img_b, None)
|
||||
# print(f'len kp_a = {len(kp_a)}, len desc_a = {len(desc_a)}')
|
||||
# print(f'type kp_b = {type(kp_b)}, type desc_b = {type(desc_b)}')
|
||||
# print(f'len kp_b = {len(kp_b)}, len desc_b = {len(desc_b) if desc_b else 0}')
|
||||
|
||||
if desc_a is None or desc_b is None:
|
||||
# rr.LOG('Error: desc_a = {}, desc_b = {}'.format(type(desc_a), type(desc_b)))
|
||||
# rr.LOG('Error: Return score 0.')
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the bruteforce matcher
|
||||
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# match.distance is a float between {0:100} - lower means more similar
|
||||
matches = bf.match(desc_a, desc_b)
|
||||
similar_regions = [i for i in matches if i.distance < 70]
|
||||
|
||||
# print('Length of similar_regions = {}'.format(len(similar_regions)))
|
||||
# print('Length of matches = {}'.format(len(matches)))
|
||||
|
||||
sorted_matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
|
||||
good_matches = sorted_matches[:int(len(sorted_matches) * 0.5)]
|
||||
similar_regions2 = [i for i in good_matches if i.distance < 70]
|
||||
# print('Length of good_matches = {}'.format(len(good_matches)))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(matches) == 0:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
return len(similar_regions) / len(matches)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Color tempertature
|
||||
code
|
||||
```
|
||||
img1 = cv2.imread(file)
|
||||
B, G, R = cv2.split(img1)
|
||||
avgB = cv2.mean(B)[0]
|
||||
avgG = cv2.mean(G)[0]
|
||||
avgR = cv2.mean(R)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# X = avgR * -0.14282 + avgG * 1.54924 + avgB * -0.95641
|
||||
# Y = avgR * -0.32466 + avgG * 1.57837 + avgB * -0.73191
|
||||
# Z = avgR * -0.68202 + avgG * 0.77073 + avgB * 0.56332
|
||||
X = 2.789 * avgR + 1.7517 * avgG + 1.1302 * avgB
|
||||
Y = 1 * avgR + 4.5907 * avgG + 0.0601 * avgB
|
||||
Z = 0 * avgR + 0.0565 * avgG + 5.5943 * avgB
|
||||
x = X / (X + Y + Z)
|
||||
y = Y / (X + Y + Z)
|
||||
n = (x - 0.3320) / (0.1858 - y)
|
||||
# n = (0.23881 * avgR + 0.25499 * avgG + -0.58291 * avgB) / (0.11109 * avgR + -0.85406 * avgG + 0.52289 * avgB)
|
||||
CCT = 449 * pow(n, 3) + 3525 * pow(n, 2) + 6823.3 * n + 5520.33
|
||||
# CCT = 437 * pow(n, 3) + 3601 * pow(n, 2) + 6831 * n + 5517
|
||||
|
||||
# print(f'x = {x}')
|
||||
# print(f'y = {y}')
|
||||
# print(f'n = {n}')
|
||||
print(f'{file}: CCT = {CCT}')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- [How to Calculate the Color Temperature / Tint of the Colors in an Image?](https://dsp.stackexchange.com/questions/8949/how-to-calculate-the-color-temperature-tint-of-the-colors-in-an-image)
|
||||
- [Calculating Color Temperature and Illuminance using the TAOS TCS3414CS Digital Color Sensor_](https://ams.com/documents/20143/80162/TCS34xx_AN000517_1-00.pdf)
|
||||
- [Java RGB转色温(CCT)](https://www.codeleading.com/article/16404945886/)
|
||||
- [Calculate color temperature (CCT) from CIE 1931 xy coordinates](https://www.waveformlighting.com/tech/calculate-color-temperature-cct-from-cie-1931-xy-coordinates)
|
||||
- [OpenCV: Color conversions](https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html)
|
||||
- [sRGB色彩空間 - 維基百科,自由的百科全書](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/SRGB%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A9%BA%E9%97%B4)
|
||||
- [Color temperature - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature#Approximation)
|
||||
- [What color is a blackbody? - some pixel rgb values](http://www.vendian.org/mncharity/dir3/blackbody/)
|
||||
2
03. Programming/OpenGL.md
Normal file
2
03. Programming/OpenGL.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
- [opengl-tutorial](http://www.opengl-tutorial.org/cn/beginners-tutorials/tutorial-1-opening-a-window/)
|
||||
- [Learn OpenGL, extensive tutorial resource for learning Modern OpenGL](https://learnopengl.com/)
|
||||
56
03. Programming/Python/argparse.ArgumentParser.md
Normal file
56
03. Programming/Python/argparse.ArgumentParser.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
一個範例:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-u", "--update_tool", default=WIN_FW_UPDATER_PATH, help="The path of win_fw_updater.exe.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-f", "--firmware", required=True, help="The path of ITB file.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-w", "--waittime_update_firmware", default=600, type=int, help="Wait time for update the firmware.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-g", "--ignore_check_file_path", action='store_true', help="Skip check the existence of file.")
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 要求user一定要設定的參數
|
||||
使用`required=True`
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-f", "--firmware", required=True, help="The path of ITB file.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
如果使用者沒有下`-f`(或者`--firmware=XXX`)就會報錯,如下:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
FwUpdateCheck.py: error: the following arguments are required: -f/--firmware
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 有設定才會產生的參數
|
||||
使用`action='store_true'`或`action='store_false'`
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-g", "--ignore_check_file_path", action='store_true', help="Skip check the existence of file.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
當使用者沒有設置`-g`時,`args.ignore_check_file_path`為`False`,當設置時,`args.ignore_check_file_path`為`True`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用預設值
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-u", "--update_tool", default="C:\\tool.exe", help="The path of win_fw_updater.exe.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
用`default=<Something>`來設定參數的預設值,上面的例子中,`args.update_tool`的預設值為`C:\tool.exe`。
|
||||
另外可以用`type=<Object type>`來指定預設值的型別。例如:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser.add_argument("-n", "--number", default=50, type=int, help="Assign a number")
|
||||
```
|
||||
上例中,`args.number`的預設值是50,型別是`int`,所以可以直接運算,不需要再經過`int(args.number)`這樣的轉換。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 限制使用者的選擇
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser.add_argument('move', choices=['rock', 'paper', 'scissors'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
使用`choices=<list>`來限定輸入的選項,上例中,使用者只能輸入'rock'、'paper'、'scissors'這三個字串中的其中一個,否則會報錯:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
error: argument move: invalid choice: 'fire' (choose from 'rock', 'paper', 'scissors')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
- https://docs.python.org/zh-tw/3/library/argparse.html
|
||||
48
03. Programming/Python/decorator.md
Normal file
48
03. Programming/Python/decorator.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
## 在decorator內取得function的default argument與class member
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
from functools import wraps
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def exampleDecorator(func):
|
||||
@wraps(func)
|
||||
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
print(f"Decorator: call by {func.__name__}")
|
||||
def get_default_args(func):
|
||||
signature = inspect.signature(func)
|
||||
return {
|
||||
k: v.default for k, v in signature.parameters.items() if v.default is not inspect.Parameter.empty
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
## Get default
|
||||
defaultKwargs = get_default_args(func)
|
||||
defaultKwargs.update(kwargs)
|
||||
print(f"Decorator: args = {args}, kwargs = {kwargs}, defaultKwargs = {defaultKwargs}")
|
||||
|
||||
objectInstance = args[0]
|
||||
if hasattr(objectInstance, 'defaultArg1'):
|
||||
print(f'objectInstance has defaultArg1, a.defaultArg1({type(objectInstance.defaultArg1)}) = {objectInstance.defaultArg1}')
|
||||
if objectInstance.defaultArg1:
|
||||
## Do something here
|
||||
print("Decorator: some message...")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('objectInstance does not have defaultArg1')
|
||||
|
||||
return func(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return wrapper
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ExampleClass():
|
||||
def __init__(self, defaultArg1=True, defaultArg2="SomeString"):
|
||||
self.defaultArg1 = defaultArg1
|
||||
self.defaultArg2 = defaultArg2
|
||||
print(f'self.defaultArg1 = {self.defaultArg1}, self.defaultArg2 = {self.defaultArg2}')
|
||||
|
||||
@exampleDecorator
|
||||
def run(self, arg1=1, arg2=2):
|
||||
print(f"ExampleClass.run(), arg1 = {arg1}, arg2 = {arg2}")
|
||||
|
||||
example = ExampleClass()
|
||||
example.run()
|
||||
```
|
||||
126
03. Programming/Python/logging.md
Normal file
126
03. Programming/Python/logging.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
### 準備
|
||||
```
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### logging level
|
||||
| level | level number | funtion |
|
||||
|:---------|:-------------|:---------------------|
|
||||
| NOTSET | 0 | |
|
||||
| DEBUG | 10 | `logging.debug()` |
|
||||
| INFO | 20 | `logging.info()` |
|
||||
| WARNING | 30 | `logging.warning()` |
|
||||
| ERROR | 40 | `logging.error()` |
|
||||
| CRITICAL | 50 | `logging.critical()` |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
|
||||
LOG_FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s'
|
||||
LOG_FILENAME = 'C:\\RobotRun\\Output\\RobotRunDocUpdater.log'
|
||||
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, filename=LOG_FILENAME, filemode='a', format=LOG_FORMAT)
|
||||
|
||||
logging.info('logging start')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Print Exception
|
||||
`logging` 模組也提供可以紀錄完整的堆疊追蹤 (stack traces),若在 `logging.error()` 加上 `exc_info` 參數,並將該參數設為 `True`,就可以紀錄 Exception,如下:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
x = 5 / 0
|
||||
except:
|
||||
logging.error("Catch an exception.", exc_info=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
也可以使用`logging.exception("Catch an exception.")`,效果跟`logging.error("Catch an exception.", exc_info=True)`一樣。
|
||||
|
||||
### 自訂 logging 輸出格式
|
||||
預設的訊息輸出格式只有 `levelname`、`name`、`message`,下面是其他相關的資訊:
|
||||
|
||||
| 格式化字串 | 說明 |
|
||||
|:------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `%(asctime)s` | 日期時間, 格式為 `YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS,ms`,例如:2018-12-13 17:20:30,567 |
|
||||
| `%(filename)s` | 模組檔名 |
|
||||
| `%(funcName)s` | 函數名稱 |
|
||||
| `%(levelname)s` | 日誌的等級名稱 |
|
||||
| `%(levelno)s` | 日誌的等級數值 |
|
||||
| `%(lineno)d` | 呼叫日誌函數所在的行數 |
|
||||
| `%(message)s` | 訊息 |
|
||||
| `%(module)s` | 模組名稱 |
|
||||
| `%(name)s` | logger 的名稱 |
|
||||
| `%(pathname)s` | 檔案的完整路徑 (如果可用) |
|
||||
| `%(process)d` | process ID (如果可用) |
|
||||
| `%(thread)d` | 執行緒 ID (如果可用) |
|
||||
| `%(threradName)s` | 執行緒名稱 |
|
||||
|
||||
例:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s'
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format=FORMAT)
|
||||
logging.debug('debug message') --> 2018-12-13 17:40:34,604 DEBUG: debug message
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 儲存log
|
||||
只要在 `logging.basicConfig()` 內的 `filename` 參數設定要儲存的日誌檔名,就可以將 logging 儲存:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
|
||||
FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s'
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, filename='myLog.log', filemode='w', format=FORMAT)
|
||||
logging.debug('debug message')
|
||||
```
|
||||
預設 `filemode` 參數是設為 `a`,代表 append (附加) 的意思,每次執行程式時,Logging 會將新的訊息加在舊的訊息後面,不會覆蓋舊的訊息。若要改成新訊息覆蓋就訊息,那可以將 `filemode` 參數設為 `w`,代表 write 的意思。
|
||||
|
||||
### 儲存log也輸出到console
|
||||
`logging`有4個主要module:
|
||||
- Logger:暴露了應用程式程式碼能直接使用的介面。
|
||||
- Handler:將(記錄器產生的)日誌記錄傳送至合適的目的地。
|
||||
- Filter:提供了更好的粒度控制,它可以決定輸出哪些日誌記錄。
|
||||
- Formatter:指明瞭最終輸出中日誌記錄的佈局。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Handler
|
||||
其中`Handlers`有以下幾類:
|
||||
1. `logging.StreamHandler` -> 控制檯輸出
|
||||
使用這個Handler可以向類似與`sys.stdout`或者`sys.stderr`的任何檔案物件(file object)輸出資訊。
|
||||
它的建構函式是: `StreamHandler([strm])` 其中`strm`引數是一個檔案物件。預設是`sys.stderr`。
|
||||
2. `logging.FileHandler` -> 檔案輸出
|
||||
和StreamHandler類似,用於向一個檔案輸出日誌資訊。不過`FileHandler`會幫你開啟這個檔案。
|
||||
它的建構函式是:`FileHandler(filename[,mode])` filename是檔名,必須指定一個檔名。 `mode`是檔案的開啟方式。預設是`'a'`,即新增到檔案末端。
|
||||
3. `logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler` -> 按照大小自動分割日誌檔案,一旦達到指定的大小重新生成檔案
|
||||
這個Handler類似於上面的`FileHandler`,但是它可以管理檔案大小。當檔案達到一定大小之後,它會自動將當前日誌檔案改名,然後建立一個新的同名日誌檔案繼續輸出。比如日誌檔案是chat.log。當chat.log達到指定的大小之後,`RotatingFileHandler`自動把 檔案改名為chat.log.1。不過,如果chat.log.1已經存在,會先把chat.log.1重新命名為chat.log.2。
|
||||
最後重新建立 chat.log,繼續輸出日誌資訊。它的建構函式是:`RotatingFileHandler(filename[, mode[, maxBytes[, backupCount]]])`,其中`filename`和`mode`兩個引數和FileHandler一樣。`maxBytes`用於指定日誌檔案的最大檔案大小。如果maxBytes為0,意味著日誌檔案可以無限大,這時上面描述的重新命名過程就不會發生。 `backupCount`用於指定保留的備份檔案的個數。比如,如果指定為2,當上面描述的重新命名過程發生時,原有的chat.log.2並不會被更名,而是被刪除。
|
||||
4. `logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler` -> 按照時間自動分割日誌檔案
|
||||
這個Handler和`RotatingFileHandler`類似,不過,它沒有通過判斷檔案大小來決定何時重新建立日誌檔案,而是間隔一定時間就自動建立新的日誌檔案。重新命名的過程與`RotatingFileHandler`類似,不過新的檔案不是附加數字,而是當前時間。它的建構函式是:`TimedRotatingFileHandler( filename [,when [,interval [,backupCount]]])`,其中`filename`引數和`backupCount`引數和`RotatingFileHandler`具有相同的意義。`interval`是時間間隔。 `when`引數是一個字串。表示時間間隔的單位,不區分大小寫。它有以下取值: S 秒 M 分 H 小時 D 天 W 每星期(`interval==0`時代表星期一) midnight 每天凌晨。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Formatters
|
||||
Formatters預設的時間格式為`%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
新增2個handler,一個輸出到螢幕上,一個寫到檔案裡。寫到檔案裡的那個handler必須是`logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler`,超過1MB時會自動分割。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import logging.handlers
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(filename) # filename就是你要存log的檔名
|
||||
|
||||
shell_print = logging.StreamHandler() # 往螢幕上輸出
|
||||
shell_print.setFormatter(format_str) # 設定螢幕上顯示的格式
|
||||
|
||||
file_print = logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler(
|
||||
filename=filename,
|
||||
mode='a',
|
||||
maxBytes=1024*1024,
|
||||
backupCount=backCount,
|
||||
encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
file_print.setFormatter(format_str) # 設定檔案裡寫入的格式
|
||||
|
||||
logger.addHandler(sh) # 把物件加到logger裡
|
||||
logger.addHandler(th)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
參考:
|
||||
- [Python - 日誌 (logging) 模組](https://titangene.github.io/article/python-logging.html)
|
||||
- [`logging` — Logging facility for Python](https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.html#module-logging "logging: Flexible event logging system for applications.")
|
||||
61
03. Programming/Python/opencv.md
Normal file
61
03. Programming/Python/opencv.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
### 將camera包裝成class
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class CameraCv(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, videoSource=0):
|
||||
self.videoSource = videoSource
|
||||
self.camera = None
|
||||
self.cameraWidth = 0
|
||||
self.cameraHeight = 0
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadHandle = None
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadStopEvent = threading.Event()
|
||||
self.lastframeRGB = None
|
||||
self.latestFrame = None
|
||||
|
||||
def start(self):
|
||||
print("Open Camera")
|
||||
self.camera = cv2.VideoCapture(self.videoSource, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
|
||||
if not self.camera.isOpened():
|
||||
raise ValueError("Unable to open video source {}".format(self.videoSource))
|
||||
|
||||
# Get video source width and height
|
||||
self.cameraWidth = self.camera.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)
|
||||
self.cameraHeight = self.camera.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)
|
||||
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadStopEvent.clear()
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadHandle = threading.Thread(target=self.collectFrame, daemon=True, args=())
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadHandle.start()
|
||||
|
||||
def stop(self):
|
||||
print("Close Camera")
|
||||
self.cameraPreviewThreadStopEvent.set()
|
||||
if self.camera.isOpened():
|
||||
self.camera.release()
|
||||
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
|
||||
|
||||
def collectFrame(self):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ret, frame = self.camera.read()
|
||||
if ret:
|
||||
# Return a boolean success flag and the current frame converted to BGR
|
||||
self.lastframeRGB = frame
|
||||
self.latestFrame = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
|
||||
|
||||
if self.cameraPreviewThreadStopEvent.is_set():
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
time.sleep(0.016)
|
||||
|
||||
def draw(self, container):
|
||||
if self.latestFrame is not None:
|
||||
container.imgtk = self.latestFrame
|
||||
container.configure(image=self.latestFrame)
|
||||
|
||||
def read(self):
|
||||
return self.camera.read()
|
||||
|
||||
def getLastFrameRgb(self):
|
||||
return self.lastframeRGB
|
||||
|
||||
def saveFrame(self, filepath):
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(filepath, self.getLastFrameRgb())
|
||||
```
|
||||
49
03. Programming/Python/subprocess.md
Normal file
49
03. Programming/Python/subprocess.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
### subprocess.Popen
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
|
||||
process = subprocess.Popen(['echo', 'More output'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
|
||||
stdout, stderr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Input arguments is a list.
|
||||
Notice `communicate()` will **block** until process was finished.
|
||||
And the output string `stdout` and `stderr` is of type `byte`. You can convert the output to `string` by:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
new_string = stdout.decode('utf-8')
|
||||
```
|
||||
or use `universal_newlines=True` in `subprocess.Popen()`. Example:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
process = subprocess.Popen(['ping', '-c 4', 'python.org'],
|
||||
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
|
||||
universal_newlines=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
The `.poll()` will return the exit code of process. If process is still running. `.poll()` will return `None`. Example:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
process = subprocess.Popen(['ping', '-c 4', 'python.org'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, universal_newlines=True)
|
||||
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
output = process.stdout.readline()
|
||||
print(output.strip())
|
||||
# Do something else
|
||||
return_code = process.poll()
|
||||
if return_code is not None:
|
||||
print('RETURN CODE', return_code)
|
||||
# Process has finished, read rest of the output
|
||||
for output in process.stdout.readlines():
|
||||
print(output.strip())
|
||||
break
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
參考:
|
||||
- [docs.python.org: `subprocess.Popen`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/subprocess.html#subprocess.Popen)
|
||||
|
||||
### subprocess.run
|
||||
`subprocess.run()`跟`subprocess.Popen()`是一樣的行為,差別是`subprocess.run()`會在process執行完畢之後才return,也就是說流程會被block住。
|
||||
`subprocess.run()`會回傳一個型別是`subprocess.CompletedProcess`的object.
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
參考:
|
||||
- [docs.python.org: _class_ `subprocess.CompletedProcess`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/subprocess.html#subprocess.CompletedProcess)
|
||||
2
03. Programming/Python/threading.md
Normal file
2
03. Programming/Python/threading.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
- [Python 多執行緒 threading 模組平行化程式設計教學 - G. T. Wang](https://blog.gtwang.org/programming/python-threading-multithreaded-programming-tutorial/)
|
||||
- [Python — 多線程. 介紹 | by Jease | Jease隨筆 | Medium](https://medium.com/jeasee%E9%9A%A8%E7%AD%86/python-%E5%A4%9A%E7%B7%9A%E7%A8%8B-eb36272e604b)
|
||||
96
03. Programming/Python/tkinter.md
Normal file
96
03. Programming/Python/tkinter.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
### 把matplotlib包裝成獨立視窗
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Plot2D(Frame):
|
||||
def __init__(self, parent, dataCollector, **kwargs):
|
||||
Frame.__init__(self, parent.mainWindow, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
self.parent = parent
|
||||
self.mainWindows = Toplevel(parent.mainWindow)
|
||||
self.mainWindows.title("AF State")
|
||||
self.figure = plt.Figure(figsize=(9,5), dpi=100)
|
||||
self.figure.suptitle('AF value plot', fontsize=16)
|
||||
self.ax = self.figure.add_subplot(111)
|
||||
self.canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(self.figure, master=self.mainWindows)
|
||||
self.canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill='both')
|
||||
self.axline = None
|
||||
|
||||
self.dataCollector = dataCollector
|
||||
self.dataCollector.start()
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
print("Plot2D close")
|
||||
self.mainWindows.destroy()
|
||||
self.dataCollector.stop()
|
||||
self.dataCollector = None
|
||||
|
||||
def draw(self):
|
||||
if self.dataCollector:
|
||||
datax, datay = self.dataCollector.getPlotData()
|
||||
self.ax.clear()
|
||||
self.ax.set_xlabel('Last {} datas'.format(self.dataCollector.getDataLength()))
|
||||
self.axline, = self.ax.plot(datax, datay)
|
||||
self.canvas.draw()
|
||||
|
||||
def getWindow(self):
|
||||
return self.mainWindows
|
||||
|
||||
def getLastData(self):
|
||||
return self.dataCollector.getLastData()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中這一行:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
self.mainWindows = Toplevel(parent.mainWindow)
|
||||
```
|
||||
是用來開一個新的視窗,其中的`parent.mainWindow`就是用`tk.TK()`所產生出來的root。
|
||||
|
||||
因為需要一直更新資料,所以需要的一個`DataCollector`來提供資料,`DataCollector`會提供畫圖需要的list,如:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
datax, datay = self.dataCollector.getPlotData()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`DataCollector`的定義如下:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class AfStateCollector(threading.Thread):
|
||||
def __init__(self, dataLength=100, pollingInterval=0.033):
|
||||
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
|
||||
self.dataLength = dataLength
|
||||
self.pollingInterval = pollingInterval
|
||||
self.stopEvent = threading.Event()
|
||||
self.data = []
|
||||
self.xdata = []
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
if self.stopEvent.is_set():
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
afValue = self.readAf()
|
||||
self.data.append(afValue)
|
||||
self.xdata.append(len(self.xdata))
|
||||
if len(self.data) > self.dataLength:
|
||||
self.data = self.data[-self.dataLength:]
|
||||
self.xdata = list(range(self.dataLength))
|
||||
|
||||
# print(f'afValue = {afValue}')
|
||||
time.sleep(self.pollingInterval)
|
||||
|
||||
print("AfStateCollector stopped.")
|
||||
|
||||
def readAf(self):
|
||||
ReadTestXUreg_cmd = "lvreg testxu read 10"
|
||||
ReadTestXUreg_cmd_process = subprocess.Popen(ReadTestXUreg_cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
|
||||
|
||||
outstring, err = ReadTestXUreg_cmd_process.communicate()
|
||||
outstring = outstring.strip().decode('utf-8')
|
||||
outstring = int(outstring, 16)
|
||||
outstring_H = (outstring & 0xFF00) / 256
|
||||
outstring_L = outstring & 0xFF
|
||||
outAFStat = int(outstring_L * 256 + outstring_H)
|
||||
|
||||
return outAFStat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- [Python GUI之tkinter視窗視窗教程大集合(看這篇就夠了) - IT閱讀](https://www.itread01.com/content/1547705544.html)
|
||||
- [【Python】改善 VideoCapture 的影像延遲 | 夏恩的程式筆記 - 點部落](https://dotblogs.com.tw/shaynling/2017/12/28/091936)
|
||||
- [Displaying a video feed with OpenCV and Tkinter - PyImageSearch](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2016/05/30/displaying-a-video-feed-with-opencv-and-tkinter/)
|
||||
96
03. Programming/Python/檢測工具.md
Normal file
96
03. Programming/Python/檢測工具.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
## 單元測試
|
||||
### [pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/7.1.x/)
|
||||
Pytest 不僅可以幫助我們運行測試,還可以幫助我們配置如何運行它們、運行哪些文件等等……Pytest 有一個配置文件 `pytest.ini`,您可以在其中描述它的配置,例如哪個版本應該是 Pytest 或者哪些是測試文件,例如下列。
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
# pytet.ini
|
||||
[pytest]
|
||||
minversion = 6.0
|
||||
addopts = -ra -q — cov=src — cov-report=html
|
||||
python_files = test_*.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### [tox](https://tox.wiki/en/latest/)
|
||||
Tox 是一個通用的virtualenv管理和測試命令行工具。
|
||||
使用不同的 Python 版本和解釋器檢查您的包是否正確安裝
|
||||
在每個環境中運行您的測試,配置您選擇的測試工具
|
||||
作為持續集成服務器的前端,大大減少樣板文件並合併 CI 和基於 shell 的測試。
|
||||
Tox 也有它的配置文件。
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
[tox]
|
||||
isolated_build = True
|
||||
envlist = py{38}
|
||||
|
||||
[testenv]
|
||||
usedevelop = true
|
||||
deps = -r src/requirements_dev.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 程式檢查工具
|
||||
用來檢查程式是否符合coding style、PEP8之類的規範
|
||||
### [pylint](https://github.com/PyCQA/pylint)
|
||||
Pylint config: create `.pylintrc` file
|
||||
```
|
||||
[MESSAGES CONTROL]
|
||||
disable=
|
||||
missing-docstring,
|
||||
too-few-public-methods[REPORTS]
|
||||
output-format=colorized
|
||||
files-output=no
|
||||
reports=no
|
||||
evaluation=10.0 - ((float(5 * error + warning + refactor + convention) / statement) * 10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### [flake8](https://github.com/pycqa/flake8)
|
||||
Flake8 config: create `.flake8` file
|
||||
```
|
||||
[flake8]
|
||||
ignore = E203, E266, E501, W503, F403, F401, E402
|
||||
max-line-length = 120
|
||||
max-complexity = 18
|
||||
select = B,C,E,F,W,T4,B9
|
||||
exclude =
|
||||
.git,
|
||||
tests
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### [mypy](http://www.mypy-lang.org/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Git hook
|
||||
### pre-commit
|
||||
Pre-commit 是一個創建 git hook的framework,以確保您的代碼編寫與您定義的代碼樣式相對應。
|
||||
它會掃描您的原始碼並運行您將在預提交配置文件中定義的所有檢查器:`.pre-commit-config.yaml`
|
||||
```
|
||||
repos:
|
||||
- repo: 'https://gitlab.com/pycqa/flake8'
|
||||
rev: 3.8.2
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: flake8
|
||||
name: Style Guide Enforcement (flake8)
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- '--max-line-length=120'
|
||||
- repo: 'https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-mypy'
|
||||
rev: v0.720
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: mypy
|
||||
name: Optional Static Typing for Python (mypy)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 漏洞檢查
|
||||
### [SonarQube](https://www.sonarqube.org/)
|
||||
有很多用於漏洞掃描的工具,但我們將看看[Sonarqube](https://www.sonarqube.org/)。Sonarqube 是用於代碼質量和安全掃描的開源強大工具,是該行業的領先工具之一。
|
||||
更多在[官方文檔](https://docs.sonarqube.org/latest/)中。
|
||||
您可以使用 Docker 映像設置本地 Sonarqube 服務器並定義`sonar-project.properties`
|
||||
```
|
||||
# must be unique in a given SonarQube instance
|
||||
sonar.projectKey=python_app_blueprint
|
||||
# --- optional properties ---
|
||||
# defaults to project key
|
||||
#sonar.projectName=My project
|
||||
# defaults to 'not provided'
|
||||
#sonar.projectVersion=1.0
|
||||
# Path is relative to the sonar-project.properties file. Defaults to .
|
||||
#sonar.sources=.
|
||||
# Encoding of the source code. Default is default system encoding
|
||||
#sonar.sourceEncoding=UTF-8
|
||||
```
|
||||
21
03. Programming/QT/Dropdown button.md
Normal file
21
03. Programming/QT/Dropdown button.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20220519094358.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
1. Button必須是QToolButton.
|
||||
2. 建立menu.
|
||||
3. 建立action.
|
||||
4. 把action加到menu裡面
|
||||
5. 把menu設定給button
|
||||
6. code example:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QMenu* saveFrameMenu = new QMenu;
|
||||
saveRawAction = new QAction(QIcon(QPixmap(":/image/resources/button-raw.png")), "SaveRaw", this);
|
||||
saveJpgAction = new QAction(QIcon(QPixmap(":/image/resources/button-jpg.png")), "SaveJpg", this);
|
||||
saveBmpAction = new QAction(QIcon(QPixmap(":/image/resources/button-bmp.png")), "SaveBmp", this);
|
||||
saveFrameMenu->addAction(saveRawAction);
|
||||
saveFrameMenu->addAction(saveJpgAction);
|
||||
saveFrameMenu->addAction(saveBmpAction);
|
||||
ui.toolButtonSaveFrame->setMenu(saveFrameMenu);
|
||||
ui.toolButtonSaveFrame->setDefaultAction(saveJpgAction);
|
||||
ui.toolButtonSaveFrame->setToolButtonStyle(Qt::ToolButtonTextBesideIcon);
|
||||
ui.toolButtonSaveFrame->setPopupMode(QToolButton::MenuButtonPopup);
|
||||
```
|
||||
9
03. Programming/QT/QVariant.md
Normal file
9
03. Programming/QT/QVariant.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
Qt有許多UI元件都可以另外設定相依的「資料」,例如`QCombobox`,這樣我們就不必老是依賴選項的文字來做許多麻煩的處理。
|
||||
例如,`QCombobox.addItem()`可以夾帶一個`QVariant`,這個`QVariant`就可以夾帶一個pointer。
|
||||
要讓`QVariant`支援`std::shared_ptr`的方式很簡單,只要在你程式的最上方加入你要使用的type就可以,例如,我要支援我自己的class AwSentinelDevice,就這樣寫:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include <memory>
|
||||
|
||||
Q_DECLARE_SMART_POINTER_METATYPE(std::shared_ptr);
|
||||
Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(std::shared_ptr<AwSentinelDevice>);
|
||||
```
|
||||
734
03. Programming/QT/Qt.md
Normal file
734
03. Programming/QT/Qt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,734 @@
|
||||
## Prepare
|
||||
### Windows 10 SDK
|
||||
下載並安裝[Windows 10 SDK](https://developer.microsoft.com/zh-tw/windows/downloads/windows-10-sdk/),安裝
|
||||
**Debugging Tools for Windows**就可以了。
|
||||
![[chrome_20210309_110223_934x685.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
然後在QtCreator裡面設置Debugger。
|
||||
![[NVIDIA_Share_20210309_110738_1920x1080.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
### Visual Studio 2017
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210312144218.png]]
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210312144242.png]]
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210312144405.png]]
|
||||
- ![[Pasted image 20210312144523.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
## PRO file 語法
|
||||
### 導入lib
|
||||
```
|
||||
QT += <lib> <lib2>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 導入include path
|
||||
```
|
||||
INCLUDEPATH += <INCLUDE_PATH>
|
||||
```
|
||||
若使用相對路徑,必須相對於makefile生成的路徑。
|
||||
也可以使用`$$PWD`來生成絕對路徑,例:
|
||||
```
|
||||
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD/../../include
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 可以用`message()`來印出變數:`message($$PWD)`
|
||||
|
||||
### 導入lib
|
||||
用`-L`指定library path,用`-l`指定libraray name。例:
|
||||
```
|
||||
LIBS += -L"../../lib" -lopencv_world320
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 指定執行目錄
|
||||
```
|
||||
DESTDIR += ../../bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 指定執行檔檔名
|
||||
```
|
||||
TARGET = <NEW_FILENAME>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Import QT pro file into Visual Studio.
|
||||
- `qmake -tp vc <QT_PROJECT_FILE>`
|
||||
- 使用VS工具import。
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本類別(class)
|
||||
### QIODevice
|
||||
An abstract class that wraps input and output for most devices
|
||||
|
||||
### QDataStream
|
||||
依序寫入的資料,也可以依序被讀出來。資料會被編碼過,所以用Text editor會看到亂碼。
|
||||
|
||||
### QTextStream
|
||||
可以依序寫入字串,也可以依序被讀出來,因為寫入的是字串,所以用Text editor就可以看到資料。
|
||||
|
||||
### QLockFile
|
||||
創造一個在操作時可以獨佔的檔案。避免race condition的情形。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QLockFile lock(fileName() +".lock");
|
||||
lock.setStaleLockTime(30000);
|
||||
|
||||
if(lock.tryLock()) {
|
||||
...
|
||||
lock.unlock();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
qInfo() << "Could not lock the file!";
|
||||
qint64 pid;
|
||||
QString host;
|
||||
QString application;
|
||||
|
||||
if(lock.getLockInfo(&pid,&host,&application)) {
|
||||
qInfo() << "The file is locked by:";
|
||||
qInfo() << "Pid: " << pid;
|
||||
qInfo() << "Host: " << host;
|
||||
qInfo() << "Application: " << application;
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
qInfo() << "File is locked, but we can't get the info!";
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### QtMessageHandler
|
||||
可以用來重新導向或攔截`qInfo()`、`qDebug()`、`qWarning()`、`qCritical()`、`qFatal()`這些function
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
const QtMessageHandler QT_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_HANDLER = qInstallMessageHandler(nullptr);
|
||||
|
||||
void lhandler(QtMsgType type, const QMessageLogContext &context, const QString &msg) {
|
||||
|
||||
QString txt;
|
||||
switch (type) {
|
||||
case QtInfoMsg:
|
||||
txt = QString("Info: %1 in %2").arg(msg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case QtDebugMsg:
|
||||
txt = QString("Debug: %1").arg(msg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case QtWarningMsg:
|
||||
txt = QString("Warning: %1").arg(msg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case QtCriticalMsg:
|
||||
txt = QString("Critical: %1").arg(msg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case QtFatalMsg:
|
||||
txt = QString("Fatal: %1").arg(msg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
(*QT_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_HANDLER)(type, context, msg);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
qInstallMessageHandler(lhandler);
|
||||
|
||||
qInfo() << "This is a info message";
|
||||
qDebug() << "This is a debug message";
|
||||
qWarning() << "This is a warning message";
|
||||
qCritical() << "This is a critical message";
|
||||
qFatal("THIS IS SPARTA!!!");
|
||||
|
||||
return a.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
也可以把這機制封裝在class裡面
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// logger.h
|
||||
#ifndef LOGGER_H
|
||||
#define LOGGER_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <QObject>
|
||||
#include <QDebug>
|
||||
#include <QFile>
|
||||
#include <QDateTime>
|
||||
#include <QDir>
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <QTextStream>
|
||||
|
||||
class logger : public QObject
|
||||
{
|
||||
Q_OBJECT
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit logger(QObject *parent = nullptr);
|
||||
|
||||
static bool logging;
|
||||
static QString filename;
|
||||
static void attach();
|
||||
static void handler(QtMsgType type, const QMessageLogContext &context, const QString & msg);
|
||||
|
||||
signals:
|
||||
|
||||
public slots:
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // LOGGER_H
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// logger.cpp
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
|
||||
QString logger::filename = QDir::currentPath() + QDir::separator() + "log.txt";
|
||||
bool logger::logging = false;
|
||||
static const QtMessageHandler QT_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_HANDLER = qInstallMessageHandler(nullptr);
|
||||
|
||||
logger::logger(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void logger::attach()
|
||||
{
|
||||
logger::logging = true;
|
||||
qInstallMessageHandler(logger::handler);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void logger::handler(QtMsgType type, const QMessageLogContext &context, const QString &msg)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Here, write log message to file
|
||||
|
||||
(*QT_DEFAULT_MESSAGE_HANDLER)(type, context, msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging category
|
||||
Logging category可以用來把輸出的log前面加上一個字串以便分類。
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include <QCoreApplication>
|
||||
#include <QDebug>
|
||||
#include <QLoggingCategory>
|
||||
|
||||
//Declare a logging category
|
||||
Q_DECLARE_LOGGING_CATEGORY(network);
|
||||
Q_LOGGING_CATEGORY(network, "network");
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
|
||||
|
||||
qInfo() << "test"; // stdout: "test"
|
||||
qInfo(network) << "test"; // stdout: "network: test"
|
||||
|
||||
//turn it off
|
||||
QLoggingCategory::setFilterRules("network.debug=false");
|
||||
|
||||
//Will not log
|
||||
qDebug(network) << This message will not shown;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!network().isDebugEnabled()) {
|
||||
QLoggingCategory::setFilterRules("network.debug=true");
|
||||
qDebug(network) << "We turned it back on";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
qDebug(network) << "You see this because you turn the message on";
|
||||
return a.exec();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## QThread
|
||||
1. 繼承自QThread。
|
||||
2. 重載`run()`。
|
||||
3. 呼叫`start()`來開始thread。
|
||||
|
||||
## QWidget
|
||||
### 設定signal與對應的slot
|
||||
1. 在class header裡面加入`Q_OBJECT`。
|
||||
2. 在constructor裡,呼叫`connect()`來建立對應關係:`connect(SOURCE_OBJECT, SIGNAL(clicked()), DEST_OBJECT, SLOT(close()))`。
|
||||
|
||||
### Postion
|
||||
1. `QRect geometry();` 取得x, y, width, height
|
||||
2. `setGeometry();` 設定x, y, width, height
|
||||
3. `x()`, `y()`, `width()`, `height()` 單獨取得x, y, width, height
|
||||
4. `move(x, y);` 只設定x, y
|
||||
5. `resize(width, height);` 只設定width, height
|
||||
|
||||
### Window state
|
||||
1. `setWindowState(Qt::WindowMaximized);`
|
||||
1. `Qt::WindowMaximized` -> `showMaximized()`
|
||||
2. `Qt::WindowMinimized` -> `showMinimized()`
|
||||
3. `Qt::WindowNoState` -> `showNormal()`
|
||||
4. `Qt::WindowFullScreen` -> `showFullScreen()`
|
||||
|
||||
### Window Style
|
||||
1. `CustomizeWindowHint()`
|
||||
2. `setWindowFlags(Qt::WindowCloseButtonHint | Qt::WindowMinimizeButtonHint)`
|
||||
1. Qt::WindowCloseButtonHint
|
||||
2. Qt::WindowMinimizeButtonHint
|
||||
3. `setWindowFlag(Qt::WindowCloseButtonHint, false)` // 取消close按鈕
|
||||
1. Qt::WindowCloseButtonHint
|
||||
2. Qt::WindowMinimizeButtonHint
|
||||
4. 沒有邊框的視窗:`setWindowFlags(Qt::FramelessWindowHint)`
|
||||
5. 透明背景: `setAttribute(Qt::WA_TranslucentBackground, true)`
|
||||
6. Style sheet: https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/stylesheet-syntax.html#style-rules
|
||||
|
||||
### Layout
|
||||
- QVBoxLayout
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QVBoxLayout* pVlayout = new QVBoxLayout();
|
||||
widget->setLayout(pVlayout);
|
||||
|
||||
// Add button to layout
|
||||
QPushButton* button = new QPushButton("My Button");
|
||||
pVlayout->addWidget(button);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `setContentsMargin()`:設定元與layout的距離
|
||||
- `setSpacing()`:設定元件與元件之間的距離
|
||||
|
||||
- QFormLayout
|
||||
- Iterate all items
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QFormLayout* layout = (QFormLayout*)this->layout();
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < layout->rowCount(); i++) {
|
||||
QLayoutItem* item = layout->itemAt(i, QFormLayout::FieldRole);
|
||||
QWidget* widget = (QWidget*)item->widget();
|
||||
|
||||
if (widget) {
|
||||
QString className = widget->metaObject()->className();
|
||||
|
||||
if (className == "QLineEdit") {
|
||||
QLineEdit* edit = (QLineEdit*)widget;
|
||||
edit->setText("Text changed");
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### QSizePolicly
|
||||
- QSizePolicly::GrowFlag:必要時可以超過
|
||||
- QSizePolicly::ExpandFlag:放到最大
|
||||
- QSizePolicly::ShrinkFlag:必要時可以小於建議尺寸
|
||||
- QSizePolicly::IgnoreFlag:忽略
|
||||
|
||||
## QLabel
|
||||
- `QLabel.setTextIneractionFlags()`:
|
||||
|
||||
## QSlider
|
||||
### Style
|
||||
#### groove
|
||||
```
|
||||
QSlider::groove {
|
||||
border: 1px solid #999999;
|
||||
height: 28px;
|
||||
background: rgba(155, 155, 155, 200);
|
||||
border-radius: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### handle
|
||||
```
|
||||
QSlider::handle {
|
||||
border: 1px solid #FF0000;
|
||||
width: 20px;
|
||||
margin: -10px 0;
|
||||
background: rgba(255, 0, 0, 200);
|
||||
border-radius: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### add-page
|
||||
```
|
||||
QSlider::add-page {
|
||||
background: rgba(255, 0, 0, 200);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### sub-page
|
||||
```
|
||||
QSlider::add-page {
|
||||
background: rgba(0, 255, 0, 200);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
![[Pasted image 20210318115725.png]]
|
||||
|
||||
## QListWidget
|
||||
- Insert a QLineEdit
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QLineEdit* lineEdit = new QLineEdit("A line edit here");
|
||||
ui->listWidget->setItemWidget(new QListWidgetItem("", ui->listWidget), lineEdit);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Insert a QSpinBox
|
||||
```
|
||||
QSpinBox* spinBox = new QSpinBox();
|
||||
ui->listWidget->setItemWidget(new QListWidgetItem("Test item 5", ui->listWidget), spinBox);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Stylesheet example
|
||||
```
|
||||
QTableView {
|
||||
selection-background-color: qlineargradient(x1: 0, y1: 0, x2: 0.5, y2: 0.5, stop: 0 #FF92BB, stop: 1 white);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
QTableView QTableCornerButton::section {
|
||||
background: red;
|
||||
border: 2px outset red;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
QTableView::indicator:unchecked {
|
||||
background-color: #d7d6d5
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## QTableWidget
|
||||
- setColumnCount()
|
||||
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtablewidget.html#setColumnCount
|
||||
- setHorizontalHeaderItem(column_index, new QTableWidgetItem("Header1"))
|
||||
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtablewidget.html#setHorizontalHeaderItem
|
||||
- setColumnWidth(column_index, column_width)
|
||||
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtableview.html#setColumnWidth
|
||||
- Bind Header's event
|
||||
- `connect(ui.tableWidget->horizontalHeader(), SIGNAL(sectionClicked(int)), this, SLOT(SectionClicked(int)));`
|
||||
|
||||
- Style
|
||||
```
|
||||
QHeaderView::section:checked{ /* Focus */
|
||||
background-color: rgba(55, 55, 55,255 );
|
||||
}
|
||||
QHeaderView::section:hover{ /* 滑鼠懸停 */
|
||||
background-color: rgba(85, 10, 10,255 );
|
||||
}
|
||||
QTableWidget{
|
||||
background-color: rgb(27, 122, 239);
|
||||
alternate-background-color: rgb(26, 81, 232);
|
||||
color:white;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## QTreeWidget
|
||||
- Data create & insert
|
||||
- `insertTopLevelItem(int index, QTreeWidgetItem*)`
|
||||
- `addTopLevelItem(QTreeWidgetItem*)`
|
||||
- `new QTreeWidgetItem(QTreeWidget*)`
|
||||
|
||||
- Insert widget
|
||||
- `void setItemWidget(QTreeWidgetItem* item, int column, QWidget* widget)`
|
||||
|
||||
- Iterate items
|
||||
- `QTreeWidgetItem* topLevelItem(int index) const`
|
||||
- `int topLevelItemCount() const`
|
||||
|
||||
- Get item
|
||||
- `QList<QTreeItemWidget*> selectedItems() const`
|
||||
|
||||
- Style
|
||||
```
|
||||
/* 有旁節點,沒有與其他元素相鄰 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:has-siblings:!adjoins-item {
|
||||
border-image: url(vline.png) 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* 有旁節點,與其他元素相鄰 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:has-siblings:adjoins-item {
|
||||
border-image: url(branch-more.png) 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* 沒有子節點,沒有旁節點,與其他元素相鄰 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:!has-children:!has-siblings:adjoins-item {
|
||||
border-image: url(branch-end.png) 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* 收合狀態,有子節點,沒有旁節點 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:closed:has-children:!has-siblings,
|
||||
/* 收合狀態,有子節點,有旁節點 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:closed:has-children:has-siblings {
|
||||
border-image: none; image: url(branch-closed.png);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* 打開狀態,有子節點,沒有旁節點 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:open:has-children:!has-siblings,
|
||||
/* 打開狀態,有子節點,有旁節點 */
|
||||
QTreeView::branch:open:has-children:has-siblings {
|
||||
border-image: none;
|
||||
image: url(branch-open.png);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## QStatusBar
|
||||
- `showMessage(QString, int miniSeconds)`: 顯示文字,一段時間後消失
|
||||
|
||||
## QToolBar
|
||||
- `addAction(QIcon, QString)`
|
||||
- `addAction(QString)`
|
||||
- `setToolButtonStyle(int)`
|
||||
|
||||
## QDockWidget
|
||||
- https://blog.csdn.net/czyt1988/article/details/51209619
|
||||
|
||||
## QJson
|
||||
- [C++(Qt5)入門範例:各種Json範例](https://lolikitty.pixnet.net/blog/post/206254516)
|
||||
|
||||
## QFile
|
||||
Read UTF-8 content from file.
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QString filename = QString::fromLocal8Bit("testplan中文檔名也可以.json");
|
||||
QFile file(filename);
|
||||
if (file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text)) {
|
||||
QTextStream fileRead(&file);
|
||||
fileRead.setCodec("UTF-8");
|
||||
|
||||
QString fileContent = fileRead.readAll();
|
||||
printf("fileContent = %s\n", fileContent.toLocal8Bit().toStdString().c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
|
||||
parseJson(fileContent);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
printf("Open failed. %s\n", filename.toLocal8Bit().toStdString().c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## String
|
||||
### UTF-8
|
||||
1. 對於n bytes的字元,第一個byte的前n個bits是1,第n+1個bit是0,第2個byte以後,都以`10`開頭。
|
||||
1. 例:
|
||||
2. 1 byte character: 0x0XXXXXXX。
|
||||
3. 2 bytes character: 0x110XXXXXX 0x10XXXXXX。
|
||||
4. 3 bytes character: 0x1110XXXXX 0x10XXXXXX 0x10XXXXXX。
|
||||
5. 4 bytes character: 0x11110XXXX 0x10XXXXXX 0x10XXXXXX 0x10XXXXXX。
|
||||
2. 例:
|
||||
1. 「A」是一個1 byte字元,編碼為`0x01000001`。
|
||||
2. 「Á」是一個2 bytes字元,編碼為`0x11000011 0x10000001`。
|
||||
3. 「好」是一個3 bytes字元,編碼為`0x11100101 0x10100101 0x10111101`。
|
||||
3. [UTF-8 to binary轉換網站](https://onlineutf8tools.com/convert-utf8-to-binary)
|
||||
2. BOM
|
||||
1. Big endian: `FE FF`
|
||||
2. Little endian: `FF FE`
|
||||
|
||||
### QString
|
||||
- 16 bits QChar(unsigned short), UNIDODE 4.0
|
||||
- `==`: compare string
|
||||
- `isNull()`: If has a value
|
||||
- `isEmpty()`: If contained value == ""
|
||||
- `QString::number()`: 接收一個數字,把數字轉為字串。
|
||||
- `QString::toInt()`、`QString::toDouble()`:把字串轉為Int或Double。
|
||||
- 讀取UTF-8的字串:
|
||||
```
|
||||
codec = QTextCodec::codecFromName("UTF-8");
|
||||
QTextCodec::setCodecForLocale(codec);
|
||||
```
|
||||
然後用`QString::fromLocal8Bit()`來讀取字串,該字串就會被當作UTF-8來處理。
|
||||
- `QTextCodec::availableCodecs()`可以列出QT所支援的格式。
|
||||
- 在Visual Studio中,強制文件用UTF-8來存檔:`#pragma execution_character_set("UTF-8")`
|
||||
- 在Visual Studio中,預設是以CP950存檔,所以字串**都不是**unicode,而是**multi-character**,所以要從Windows讀進來的字串,一律需要使用`QString::fromLocal8Bit("")`,而一旦轉為QString之後,就是UTF-8了,若需要再輸出回Windows,則需要`QString.toLocal8Bit().toStdString()`。
|
||||
- 例:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
QString filename = QString::fromLocal8Bit("testplan中文檔名也可以.json");
|
||||
QFile file(filename);
|
||||
if (file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text)) {
|
||||
QTextStream fileRead(&file);
|
||||
fileRead.setCodec("UTF-8");
|
||||
|
||||
QString fileContent = fileRead.readAll();
|
||||
printf("fileContent = %s\n", fileContent.toLocal8Bit().toStdString().c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
|
||||
parseJson(fileContent);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
printf("Open failed. %s\n", filename.toLocal8Bit().toStdString().c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Visual Studio 2017 debug QString: [调试时直接显示QString的字符值(包含windows和linux)](https://blog.csdn.net/iamdbl/article/details/78343642)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Search
|
||||
- `QString.indexOf()`
|
||||
- `QString.lastIndexOf()`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Trim
|
||||
- `QString.chop(5)`:去掉結尾的5個字元,inplace轉換,沒有回傳新字串。
|
||||
- `QString.left(5)`:取最左邊5個字元
|
||||
- `QString.right(5)`:取最右邊5個字元
|
||||
|
||||
#### Replace
|
||||
- `QString.replace("original", "new")`:將"original"替換為"new"。
|
||||
- 也支援regular expression
|
||||
|
||||
#### Split
|
||||
- `QString.split(",")`:用","把字串分割,並回傳一個`QStringList`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Regular Expression
|
||||
- `.`:匹配任意1個字元
|
||||
- `+`:此類型的匹配字元可以1個以上
|
||||
- `*`:匹配任意多個字元
|
||||
- `^`:表示開始位置
|
||||
- `$`:表示結束位置
|
||||
- `?`:表示前一個匹配條件不一定要成立
|
||||
- `[]`:用括號來限制要匹配的字元
|
||||
|
||||
## Event
|
||||
- 如果有特殊需求,可以重載`QWidget::event(QEvent*)`來達成。
|
||||
|
||||
### MouseEvent
|
||||
- Get coordinate of component: `QMouseEvent::x()` & `QMouseEvent::y()`
|
||||
- Get coordinate of window: `QMouseEvent::windowPos().x()` & `QMouseEvent::windowPos().y()`
|
||||
- Get coordinate of screen: `QMouseEvent::screenPos().x()` & `QMouseEvent::screenPos().y()`
|
||||
- `QPoint mapToGlobal(QPoint)`: Translates the widget coordinate pos to global screen coordinates.
|
||||
- `QCursor::pos().x()` & `QCursor::pos().x()`: 也可以獲得screen coordinate。
|
||||
- Get click
|
||||
```
|
||||
if (mouseEvent->buttons() & Qt::LeftButton) // or Qt::RightButton, Qt::MiddleButton
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### MouseCursor
|
||||
- 設定cursor click的位置:`QCursor cursor = QCursor(pixmap, -1, -1)`
|
||||
- (-1, -1) 表示用cursor中心點為click點
|
||||
- ( 0, 0) 表示用cursor左上角為click點
|
||||
- 更換cursor:`setCursor(Qt::ArrowCursor)`
|
||||
|
||||
### ResizeEvent
|
||||
- `void resizeEvent(QResizeEvent*)`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## QOpenGLWidget
|
||||
- `void paintGL()`
|
||||
- `void initialGL()`
|
||||
- `void resizeGL(int w, int h)`
|
||||
|
||||
## QGLShaderProgram
|
||||
- `addShaderFromSourceCode`
|
||||
- `bindAttributeLocation`:設定傳入的變數
|
||||
- `uniformLocation`:取得變數
|
||||
|
||||
## GL概念
|
||||
### Vertex
|
||||
#### Coordinate
|
||||
```
|
||||
float *vertexData = new float[12] {
|
||||
1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
-1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
-1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Texture
|
||||
#### Coordinate
|
||||
材質座標永遠都在第一象限
|
||||
```
|
||||
float* textureVertexData = new float[8] {
|
||||
1.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
0.0f, 0.0f,
|
||||
1.0f, 1.0f,
|
||||
0.0f, 1.0f,
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 建立材質
|
||||
- `glGenTextures(1, t);`
|
||||
- `glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, *t);`
|
||||
- `glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);`
|
||||
- `glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);`
|
||||
|
||||
#### 寫入材質
|
||||
- `glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);`
|
||||
- `glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, idY);`
|
||||
- `glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, pixelW, pixelH, 0, GL_LUMINANCE, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, plane[0]);`
|
||||
```
|
||||
glTexImage2D(
|
||||
GL_TEXTURE_2D,
|
||||
0, // 細節,預設0
|
||||
GL_LUMINANCE, // GPU內部格式
|
||||
pixelW,
|
||||
pixelH,
|
||||
0,
|
||||
GL_LUMINANCE, // Pixel format
|
||||
GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, // Data format
|
||||
plane[0]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `glTexSubImage2D()`:修改texture
|
||||
- `glUniform1i(textureUniformY, 0);`
|
||||
- `glDrawArray(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, 4);`
|
||||
|
||||
## GLSL
|
||||
|
||||
### 內建變數
|
||||
- `gl_FragColor`
|
||||
|
||||
### 3種變數類型
|
||||
- `varying`:vertex與shader共用,vertex運算完之後傳給shader使用。
|
||||
- `attribute`:vertex使用,由`bindAttributeLocation`傳入
|
||||
- `uniform`:由user傳入的資料,由`uniformLocation`得到pointer address,再由`glUniform1i(textureUniformY, 0)`來設定。
|
||||
|
||||
### Vertex Shader
|
||||
```
|
||||
attribute vec4 vertexIn;
|
||||
attribute vec2 textureIn;
|
||||
varying vec2 textureOut;
|
||||
|
||||
void main() {
|
||||
gl_position = vertexIn;
|
||||
textureOut = textureIn;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Fragment Shader
|
||||
```
|
||||
varying vec2 textureOut;
|
||||
uniform sampler2D texY;
|
||||
uniform sampler2D texU;
|
||||
uniform sampler2D texV;
|
||||
|
||||
void main() {
|
||||
vec3 yuv;
|
||||
vec3 rgb;
|
||||
|
||||
yuv.x = textue2D(texY, textureOut).r;
|
||||
yuv.y = textue2D(texU, textureOut).r - 0.5;
|
||||
yuv.z = textue2D(texV, textureOut).r - 0.5;
|
||||
rgb = mat3(
|
||||
1, 1, 1,
|
||||
0, -0.39465, 2.03211,
|
||||
1.13983, -0.5806, 0) * yuv;
|
||||
gl_FragColor = vec4(rgb, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### APIs
|
||||
畫出矩形與材質
|
||||
- `glVertexAttribPointer(ATTRIB_VERTEX, 2, GL_FLOAT, 0, 0, vertexVertices);`
|
||||
- `glEnableVertexAttribArray(ATTRIB_VERTEX);`
|
||||
- `glVertexAttribPointer(ATTRIB_TEXTURE, 2, GL_FLOAT, 0, 0, textureVertices);`
|
||||
- `glEnableVertexAttribArray(ATTRIB_TEXTURE);`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 檔案操作
|
||||
## 開啟檔案對話框
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
QString selectedFilepath = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(
|
||||
this,
|
||||
tr("Select test plan file"), // 檔案選擇對話框左上角的提示
|
||||
tr("."), // 檔案選擇對話框一開始的路徑
|
||||
"(*.json);;All files(*.*)"); // 可選擇的副檔名
|
||||
```
|
||||
使用者所選擇的檔名會放在`selectedFilepath`,可以用`selectedFilepath.isEmpty()`來判斷使用者是不是真的有選擇檔案或是按了取消鍵。
|
||||
|
||||
## 存檔對話框
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(
|
||||
this,
|
||||
tr("Save Address Book"), "", // 檔案選擇對話框左上角的提示
|
||||
tr("Address Book (*.abk);;All Files (*)")); // 存檔的副檔名
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# MISC
|
||||
## 教學文
|
||||
- [Qt教程,Qt5编程入门教程(非常详细)](http://c.biancheng.net/qt/)
|
||||
130
03. Programming/UML.md
Normal file
130
03. Programming/UML.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
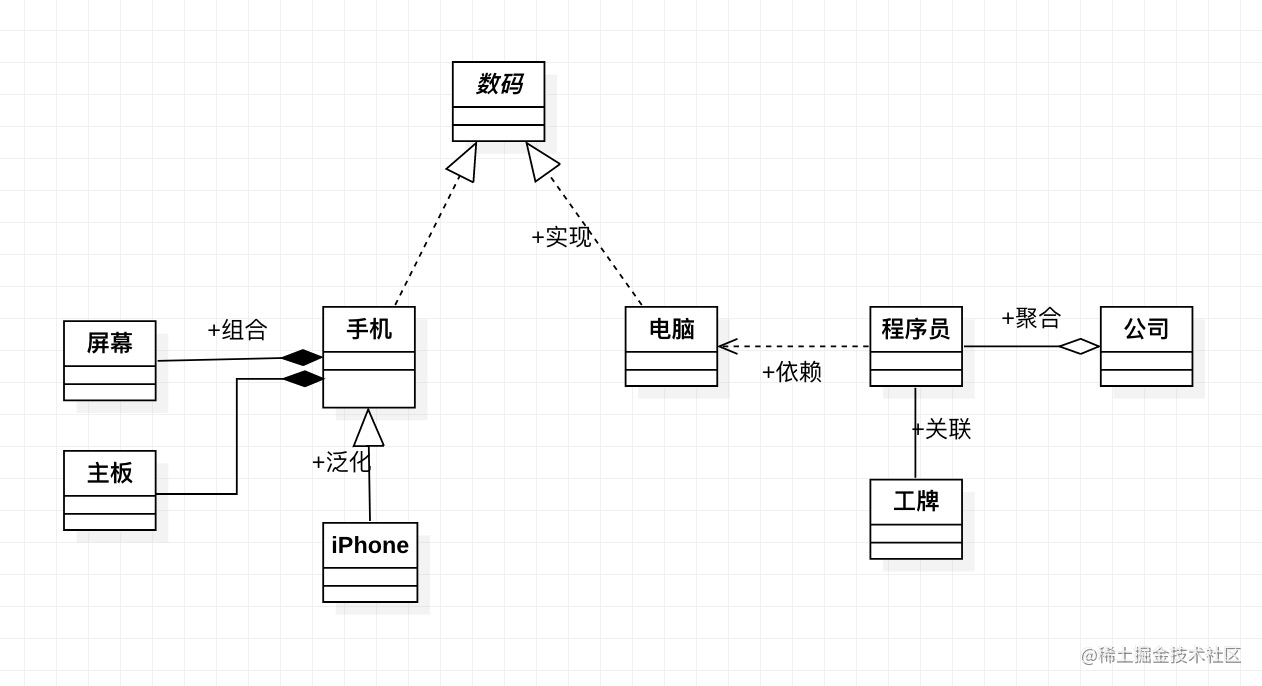
|
||||
|
||||
玩轉設計模式 - 看懂UML類圖
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
前言
|
||||
--
|
||||
|
||||
作為設計模式系列的第一篇,我準備先分享下如何看懂UML類圖,看完這篇文章,你就能看懂類圖中各個類之間的關係以及線條、箭頭都代表什麼意思。 同時,我們會將類圖所表達的含義和最終的代碼實現對應起來; 有了這些知識,看後面章節的設計模式結構圖就沒有什麼問題了。
|
||||
|
||||
先看一個例子
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我畫的一張類圖,使用的工具是StarUML,Mac版本[下載地址](https://macwk.com/soft/staruml)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 數碼是斜體的,表示數碼是一個抽象類
|
||||
- 數碼有兩個繼承類,分別是手機和電腦,他們之間的關係是**實現**關係,用帶空心箭頭的虛線表示
|
||||
- iPhone與手機之間也是繼承關係,他們之間的關係是**泛化**關係,用帶空心箭頭的實線表示
|
||||
- 手機由屏幕和主板等組合而成,他們之間的關係是**組合**關係,用帶實心菱形的實線表示
|
||||
- 程序員上班必須要用電腦,他們之間的關係是**依賴**關係,用帶箭頭的虛線表示
|
||||
- 程序員與公司之間是**聚合**關係,用帶空心菱形的實線表示
|
||||
- 程序員一般都會有自己的工牌,他們之間的關係是**關聯**關係,用實線表示
|
||||
|
||||
以上例子和圖中我都把類的六種關係特別標註出來了,下面我們具體講講這六種關係
|
||||
|
||||
類之間的關係
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
類的繼承結構表現在UML中為:**實現**和**泛化**
|
||||
|
||||
繼承關係為 is-a的關係;兩個對象之間如果可以用 is-a 來表示,就是繼承關係
|
||||
|
||||
### 實現(Realization)
|
||||
|
||||
“數碼”是一個抽象概念,在現實中並不能直接用來定義對象,必須指明它的子類,比如手機和電腦。“數碼”這個類在java中可以用接口或者抽象類表示,在C++中用抽象類表示。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:實現關係表現為繼承抽象類。
|
||||
|
||||
### 泛化(Generalization)
|
||||
|
||||
手機在現實中有實現,可以用來定義具體的對象,iphone是手機的子類,手機和iphone的關係為泛化關係。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:泛化關係表現為繼承非抽象類。
|
||||
|
||||
### 聚合(Aggregation)
|
||||
|
||||
聚合表示兩個對象之間是整體和部分的**弱關係,生命週期不同步**,部分的生命週期可以超越整體,比如程序員和公司,公司倒閉了,但程序員還在,還可以去其他公司。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:聚合關係以**成員變量**的形式實現,只是成員變量的賦值時機是在**類方法**裡,代碼如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//第一種是在set方法裡直接設置子類的實例
|
||||
class Company {
|
||||
private Programmer programmer;
|
||||
|
||||
public void setProgrammer(JavaProgrammer javaProgrammer) {
|
||||
programmer = javaProgrammer;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//第二種方式是在set方法裡直接寫死,直接定義一個初始值
|
||||
class Company {
|
||||
private Programmer programmer;
|
||||
|
||||
public void setProgrammer() {
|
||||
programmer = new JavaProgrammer();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
複製代碼
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 組合(Composition)
|
||||
|
||||
組合表示兩個對象之間是整體和部分的**強關係,生命週期一致**,部分的生命週期不能超越整體,或者說組合中的整體不能缺少部分。就像手機不能缺少屏幕和主板一樣。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:組合關係以**成員變量**的形式實現,只是成員變量的賦值時機是在**類構造方法**裡,代碼如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//手機由屏幕組成
|
||||
class Phone {
|
||||
private Screen screen;
|
||||
|
||||
//創建手機的時候同時創建屏幕
|
||||
public Phone() {
|
||||
screen = new Screen();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
複製代碼
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 關聯(Association)
|
||||
|
||||
關聯表示的是兩個不同對象之間存在的固定的對應關係,**它是一種靜態關係,和運行狀態無關**。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:關聯關係也是以成員變量的形式實現,只是成員變量的賦值時機是在聲明這個變量的時候,代碼如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//程序員都會有工牌
|
||||
class Programmer {
|
||||
private Card card = new Card();
|
||||
}
|
||||
複製代碼
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 依賴(Dependency)
|
||||
|
||||
依賴表示的是**一個對象在運行期間會用到另一個對象的關係**,與關聯關係不同的是,它是一種臨時性的關係,通常在**運行期間**產生,並且隨著運行時的變化,依賴關係也可能發生變化。比如程序員在工作的時候會用到電腦,程序員是依賴電腦的。
|
||||
|
||||
代碼實現:依賴關係主要可以通過**方法參數、方法局部變量、靜態方法**三種方式實現,方法參數代碼如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Programmer {
|
||||
//程序員工作的時候需要用到電腦
|
||||
public void work(Computer computer) {
|
||||
computer.work();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
複製代碼
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
總結
|
||||
--
|
||||
|
||||
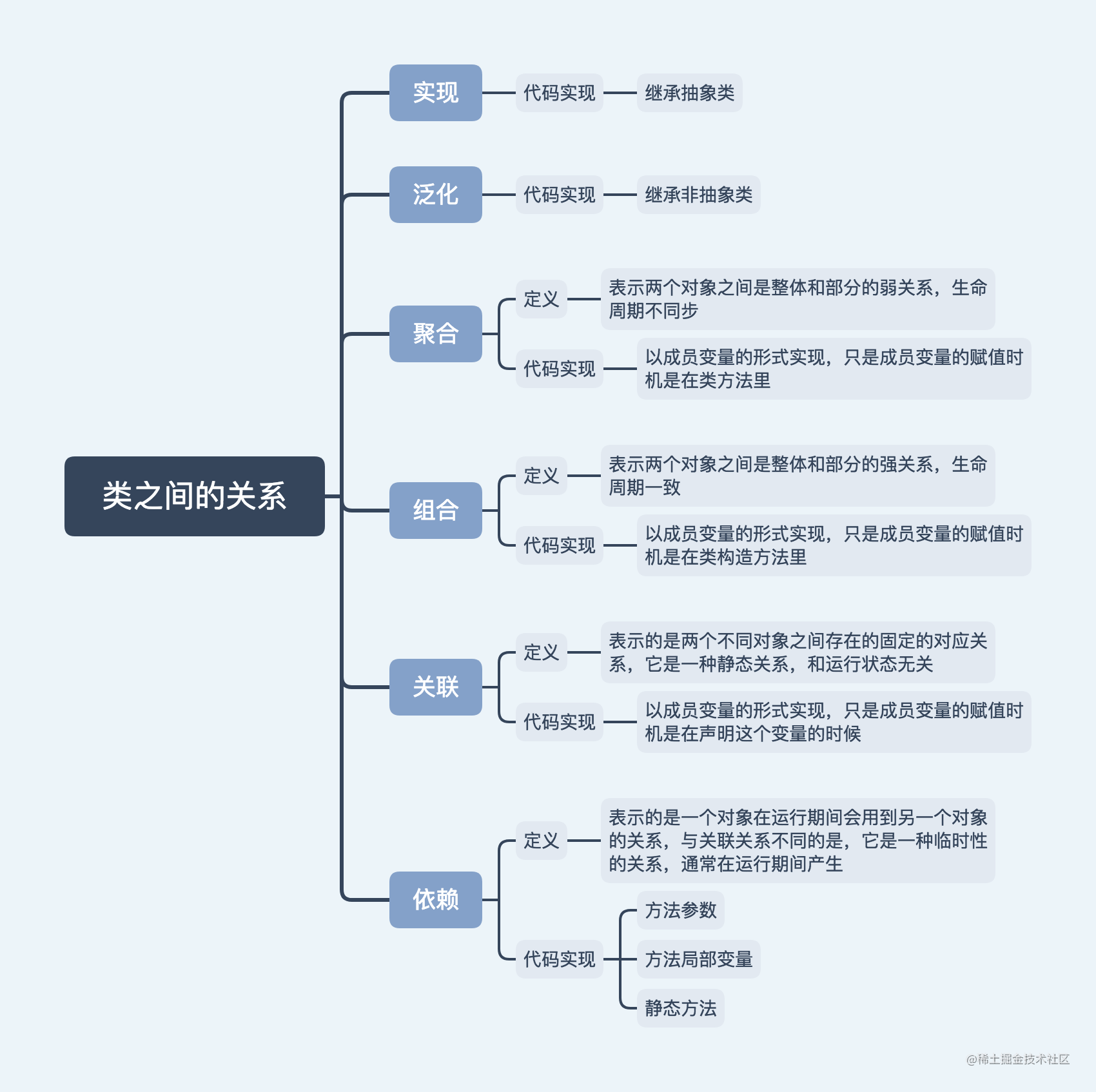
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-----
|
||||
- [玩轉設計模式 - 看懂UML類圖](https://juejin.cn/post/6914946238756421639)
|
||||
2
03. Programming/演算法.md
Normal file
2
03. Programming/演算法.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
# 介紹文
|
||||
- [VisuAlgo - visualising data structures and algorithms through animation](https://visualgo.net/en?fbclid=IwAR1b6wbTcgKJg3T14ehAPMpHO_QWvnj1evMxrshrAvqukHH2ZPXJUWgAvd4)
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user